by Fishgate@sanap | May 10, 2019 | Announcement, Fellowship, News, Research, Science
The information below was sent through by the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research.
SCAR Fellowship Scheme, partnerships and new opportunities in 2019

The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR), the Council of Managers of National Antarctic Programs (COMNAP), and the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) have been working together for many years to support talented early-career researchers, scientists, engineers, environmental managers, and other professionals to strengthen international capacity and cooperation in fields such as science support and facilitation, environmental management implementation, and climate, biodiversity, conservation, humanities and astrophysics research by way of an annual funding opportunity.
For 2019, these Antarctic organisations are joined by the International Association of Antarctica Tour Operators (IAATO) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), who will each support additional Antarctic-related fellowships.
SCAR Launches Antarctic Fellowship Opportunities for 2019
SCAR today launches its 2019 Antarctic-related Fellowships for early-career researchers. SCAR will offer 5 to 6 fellowships of up to USD $15,000 each for 2019, with additional support for the scheme having been provided by India, Korea and France. A new SCAR/WMO Fellowship is also available in 2019 as detailed below. The Fellowships enable early-career researchers to join a project team from another country, opening up new opportunities and often creating partnerships that last for many years and over many Antarctic field seasons. The deadline for fellowship applications is 17 July 2019.
Additional opportunities in 2019 through the SCAR Fellowship scheme
For 2019 there are a number of extra opportunities through the SCAR scheme, with some restrictions on applicability but using the standard application process for SCAR Fellowships:
- India is providing support to fund one full SCAR Fellowship, with France providing a contribution to the Fellowship funds.
- The Republic of Korea will also contribute to one Fellowship to be allocated to an applicant from a country which has been under-represented within the SCAR Fellowship scheme to date.
- For the new SCAR/WMO Fellowship, the WMO and SCAR will jointly fund one Fellowship for applicants from a WMO country who meet the Fellowship eligibility criteria of the WMO.
COMNAP and IAATO have already launched their Fellowship scheme for 2019 and CCAMLR launch their Scholarship scheme with two deadlines in 2019. Details are available at : https://www.scar.org/community-news/fellowship-opportunities-launched/
Background information:
The SCAR scheme is launched today, noting the complementary schemes of our partners – the COMNAP and IAATO Fellowship Scheme and the CCAMLR Scientific Scholarship Scheme. Full details of these schemes are available on their respective websites below.
For more information on SCAR Fellowships, visit the SCAR website at:
www.scar.org/awards/fellowships/information/
For information on the COMNAP and IAATO Fellowships, visit the COMNAP website at:
www.comnap.aq/SitePages/fellowships.aspx
For information on CCAMLR Scholarships, visit the CCAMLR website at:
www.ccamlr.org/en/science/ccamlr-scientific-scholarship-scheme

by Fishgate@sanap | Apr 30, 2019 | Announcement, News, Science
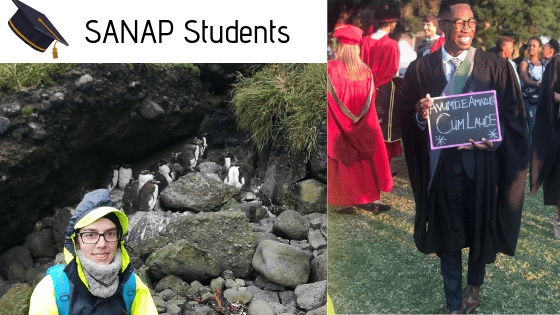
Congratulations to Daniela Monsanto and Mthoko Twala, two SANAP students completing their Masters degrees, both with cum laude, within the field of biology.
Daniela completed her degree at the University of Johannesburg, under the supervision of Prof Bettine van Vuuren. This Masters was part of the SANAP project: Biocomplexity: Understanding biological patterns in space and time. Daniela examined fine-scale spatial genetic patterns in one of the most dominant and ecologically significant soil organisms across the sub-Antarctic region, the Collembola Cryptopygus antarcticus. Her work highlighted a genetic discontinuity, which when overlaid onto a detailed geomorphological map of the area, coincided with a 3 meter ridge (for Collembola, this height is equivalent to a human scaled to 2.5 times the height of Table Mountain).
Mthoko completed his degree at the University of Pretoria, under the supervision of Dr Michelle Greve. This Masters was part of the SANAP project: Invasions in the changing sub-Antarctic. Mthoko assessed whether the invasive plant, Sagina procumbens, disproportionately benefits other invasive species on Marion Island. He found mixed results, with invasive plants necessarily benefitted from Sagina, but invasive collembolans benefitting more than native collembolans.
Congratulations to the students, as well as the supervisors.
See below these achievements announced on social media.
https://www.facebook.com/AntarcticLegacySA/posts/853552648317012
https://www.facebook.com/AntarcticLegacySA/posts/854122318260045
Anché Louw, Antarctic Legacy of South Africa, 30 April 2019

by Fishgate@sanap | Apr 16, 2019 | Research, Science, Southern Ocean, sub-Antarctic
Our Wave Gliders have arrived back from the Southern Ocean. Last Friday 5th April we picked up our second carbon Waveglider WG027 a few tens of metres from the breakwater in Granger Bay at the end of an exciting but problem free transit of 1500km from the Sub-Antarctic Zone (43oS 8oE)(Video). Its twin WG052 had completed its even longer transit of 2800km from the Polar Upwelling Zone (54oS OoE) 9 days earlier. Both units arrived in excellent shape in what was a first for us, bringing our gliders home with a ship pick-up. Both gliders completed 4-month long missions of which 10 weeks were sampling at their respective locations and 6 weeks transiting back to Cape Town.
VIDEO: WG052 waiting to be picked up off Granger Bay in a cold misty morning in Cape Town a couple of weeks ago after its 2800km epic from 54oS.
https://www.facebook.com/AntarcticLegacySA/videos/322703648445517/
Bringing the gliders home under their own means opens the door towards the direction of reducing the dependency on ships and reduces the long-term costs of long-term observations. It is a significant technical challenge for the robots and the engineers. The biggest problems we encountered, apart from the vicious storms, were the very strong mesoscale jets west of the Agulhas retroflection area. Jets with flow speeds of over 2kn posed navigation challenges for the pilots but we also learned much from the experience and despite a few necessary deviations (Figure 1a,b) that probably added a week to the transit we got them home in really good shape (Figure 2).
The decision to bring them home was shaped by two main considerations: firstly, we wanted to avoid the expensive physical damage to the gliders that often happens with ship recovery, especially under the typically rough conditions in the Southern Ocean. As it turned out we made the right call especially for WG052 which would have been all but impossible to retrieve such were the conditions. Secondly, we wanted to evaluate if wave gliders can be combined to address mesoscale differences in the response of the ocean to synoptic scale atmospheric forcing.
As mentioned in earlier posts each of these gliders was paired with a buoyancy glider over the entire period of deployment at their respective long-term observational sites in the SAZ and the PUZ as part of two NRF-funded SOCCO SOSCEX-Storm projects. This pairing enabled us to simultaneously observe the air-sea fluxes of CO and the ocean physics dynamics that influence them in the upper 1000m of the ocean. This is necessary because it is not clear how important these ocean dynamics are in predicting the climate sensitivity of the carbon cycle in the Southern Ocean. This learning will be used to improve the Earth System Models used to predict regional and global climate change, particularly the South African CSIR-VrESM model being developed as a collaboration between SOCCO, Global Change Institute-Wits University and the MaRe Institute at UCT.
All the instruments were fully operational over the entire time and the initial look at the data suggests that we have excellent accuracy and precision. This was the first operational test for our newly developed VeGAS pCO2 units on both gliders and we will do a deep dive into the data later this week.
This science work would not have been possible without the expertise and dedication of our engineering partners at Sea Technology Services who run SA-RobOTIC and their student engineers.
– Dr. Pedro M. Scheel Monteiro & SOCCO & SA-RobOTIC team, 08 April 2019 (posted 16 April 2019)

by Fishgate@sanap | Mar 31, 2019 | Announcement, Antarctica, Important Dates, News, Research, Science

SCAR Event Announcement
XIII International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Sciences
The abstract submission deadline for the XIII International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Sciences has been extended to 21 April 2019.
Please go to the event website (click here) for more information.

by Fishgate@sanap | Mar 25, 2019 | Antarctica, Important Dates, SANAE, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean, sub-Antarctic

Interested in the South African Research and Supply Vessel, the S.A. Agulhas II 2019 Voyage Schedule?
Click here.

by Fishgate@sanap | Mar 15, 2019 | Antarctica, News, Research, SANAE, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean
Welcome to Cape Town SANAE57 team, take-over personnel, Weddell Sea Expedition crew, Department of Public Works personnel and Nolitha Construction (responsible for the refurbishments of the SANAE IV base), the Ultimate Helicopter Crew and the S.A. Agulhas II’s Captain and Crew.
The 57th South African National Antarctic Expedition (SANAE) team has returned to Cape Town, after 15 months away from home (see photo below). This team had to stay a bit longer at SANAE IV than usual, due to the longer take-over in order to accommodate the Weddell Sea Expedition, that was incorporated in the 2018/2019 Antarctica Cruise.

L-R (Back): Stephanus Schoeman (RADAR Engineer), John Skelete (Diesel Mechanic), Bo Orton (Electrician), Will Jelbert (Doctor), Forster Mashele (VLF Engineer), Sabelo Biyela (Diesel Mechanic); (front) Hloni Rakoteli (Communications Engineer), Lux Tanyana (Base Engineer), Elias Seabi (Meteorological Technician) and Cobus van der Merwe (Neutron Engineer).
This Weddell Sea Expedition was funded by the The Flotilla Foundation and the S.A. Agulhas II chartered a team of scientists into the Weddell Sea, for extensive scientific exploration on and around the LarsenC ice shelf and the A68 Iceberg. Click here to meet the South Africans that was part of this expedition.
The Weddell Sea Expedition also involved the search for Sir Ernest Shackleton’s ship, the Endurance (click here for more information), but due to unfavourable weather conditions and the loss of the AUV (automated underwater vehicle) the search was ended where after the ship headed back to Penguin Bukta where overwintering members (S57) and take-over personnel of SANAE IV boarded the ship.
The welcoming ceremony was led by Mathibela Selepe (Department of Environmental Affairs, Chief Engineer: Telecommunications and Instrumentation) and welcoming speech delivered by Mbulelo Dopolo (Department of Environmental Affairs, Branch: Oceans and Coasts, Director: Earth Systems Strategies).
Anché Louw, Antarctic Legacy of South Africa, 15 March 2019
https://www.facebook.com/AntarcticLegacySA/videos/vl.317523262441303/800923453598499/?type=1