
by Ria Olivier | Nov 12, 2025 | Announcement, Research, SANAP, SCAR, Science
Recognising Excellence in Antarctic Research and Service
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) plays a pivotal role in advancing knowledge of the Antarctic and Southern Ocean. A cornerstone of this mission is the recognition of excellence — celebrating researchers and contributors whose work and service embody the spirit of international cooperation and scientific discovery in the Antarctic community.
 Honouring Outstanding Contributions
Honouring Outstanding Contributions
To highlight and reward those who exemplify the best of the Antarctic community, SCAR established a series of prestigious medals. These awards celebrate both scientific achievement and dedicated service, serving as an inspiration for the next generation of polar researchers.
Since their inception in 2006, SCAR has awarded:
In 2018, SCAR introduced a third category:
Each of these medals is awarded through a peer-nominated process, ensuring fairness, transparency, and the recognition of true merit. Recipients are selected by an expert committee based on their outstanding contributions to Antarctic research, collaboration, or education and outreach.
The President’s Medal for Outstanding Achievement
In addition to the main medals, SCAR also awards the President’s Medal for Outstanding Achievement. This distinguished honour is presented by the outgoing SCAR President to an individual who has made exceptional contributions to SCAR and the wider Antarctic community during their term.
Call for Nominations — 2026 SCAR Medals
Nominations for the 2026 SCAR Medals are now open!
🗓️ Initial nominations close on 22 March 2026.
This is a unique opportunity to recognise peers who have made remarkable contributions to Antarctic science, coordination, or communication.
For detailed information on the award criteria and selection process, please visit SCAR’s Detailed Information page.

by Ria Olivier | Nov 11, 2025 | Announcement, Research, SANAP, SANAP Student, Science
At the edge of the Earth lies a mirror of our planet — a place where ice tells the story of climate, oceans, and life itself. The South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP) stands at the forefront of exploring and protecting this frozen world.
This November, the SANAP research community will gather once again for the 7th SANAP Symposium, a meeting of minds, science, and purpose.
Dates: 16–19 November 2025
Venue: Kwalata Game Reserve, South Africa
The Symposium brings together researchers, students, policymakers, and environmental stewards from across disciplines to share discoveries from the Antarctic and Southern Ocean, and to reflect on how they shape our understanding of global change.
From the southernmost ice sheets to Africa’s beating heart, SANAP researchers explore the connections that link polar science to climate, ecosystems, and society. The Symposium offers a unique opportunity to discuss new research, inspire collaboration, and strengthen the community committed to safeguarding the world’s most remote environments.
Join the conversation, connect with fellow explorers of knowledge, and be part of shaping a sustainable polar future.
More information click here

by Ria Olivier | Oct 15, 2025 | Announcement, Gough Island, Humanities, SANAP
 After more than a year on the remote and rugged shores of Gough Island, the Gough 70 Overwintering Team has safely arrived back in Cape Town today — marking the end of another remarkable chapter in South Africa’s contribution to global environmental and climate research.
After more than a year on the remote and rugged shores of Gough Island, the Gough 70 Overwintering Team has safely arrived back in Cape Town today — marking the end of another remarkable chapter in South Africa’s contribution to global environmental and climate research.
 The team has spent the past year maintaining and operating the South African weather and research station on Gough Island, one of the most isolated and scientifically significant islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. Their work forms a vital part of the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), contributing to international understanding of climate systems, ocean–atmosphere interactions, and biodiversity conservation in one of the world’s most pristine environments. Throughout their 13-month stay, the Gough 70 team challenged weather conditions, isolation, and logistical difficulties — yet continued to deliver crucial meteorological observations and research support. Their dedication and resilience embody the true spirit of the SANAP community.
The team has spent the past year maintaining and operating the South African weather and research station on Gough Island, one of the most isolated and scientifically significant islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. Their work forms a vital part of the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), contributing to international understanding of climate systems, ocean–atmosphere interactions, and biodiversity conservation in one of the world’s most pristine environments. Throughout their 13-month stay, the Gough 70 team challenged weather conditions, isolation, and logistical difficulties — yet continued to deliver crucial meteorological observations and research support. Their dedication and resilience embody the true spirit of the SANAP community.
 We extend a heartfelt welcome home to each member of the team and express our thanks for their commitment and hard work. Their efforts not only uphold South Africa’s legacy of excellence in polar and sub-Antarctic research but also ensure that critical data continues to support global scientific collaboration. (above taken when arriving at Gough Island in 2024)
We extend a heartfelt welcome home to each member of the team and express our thanks for their commitment and hard work. Their efforts not only uphold South Africa’s legacy of excellence in polar and sub-Antarctic research but also ensure that critical data continues to support global scientific collaboration. (above taken when arriving at Gough Island in 2024)
As the team reunites with family and friends, the Gough 71 Overwintering Team now takes up the baton, continuing the mission on the island for the year ahead.
Welcome back, Gough 70 — and thank you for your service and passion for discovery in one of the most remote corners of the world.
— The SANAP Community

by Ria Olivier | Sep 25, 2025 | Announcement, Jobs, Marion Island, News, Overwintering Team, Research, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean, Stations, sub-Antarctic, Team member

The following positions are available on the sub-Antarctic, Marion Island for the overwintering period (April 2026 to May 2027)
Environmental Officer Assistant Environmental Officer
Communications Engineer Diesel Mechanic Electrical Engineer Medical Orderly
Senior Meteorological Technician Assistant Meteorological Technician
Closing Date: 06 OCTOBER
The incumbent will execute duties at a Sub/Antarctic Base and adhere to the health, safety and environmental requirements. The successful applicant will spend a full year (April 2026 to May 2027) at Marion Island. There is no option to return to South Africa before May 2027. The ability to work and live with small groups of people is thus essential. Although the base is well-equipped with e-mail, fax and satellite telephone facilities, the applicant must be self-sufficient and self-motivated.
Click here: View all positions

by Ria Olivier | Aug 25, 2025 | Research, SANAP, South Atlantic, Southern Ocean
 Pelagic High Seas Ocean Ecoregionalisation of the Indian Subantarctic (PHOCIS) will be holding a workshop in Cape Town, South Africa, 25 – 29 August 2025. The main objectives for the Cape Town workshop will be for participants to present and discuss progress on all PHOCIS work packages, but in particular to advance WP4 on Integrated Ocean Management (this study), and WP5 on Research and Monitoring.
Pelagic High Seas Ocean Ecoregionalisation of the Indian Subantarctic (PHOCIS) will be holding a workshop in Cape Town, South Africa, 25 – 29 August 2025. The main objectives for the Cape Town workshop will be for participants to present and discuss progress on all PHOCIS work packages, but in particular to advance WP4 on Integrated Ocean Management (this study), and WP5 on Research and Monitoring.
 The PHOCIS project, “Pelagic High Seas Ocean Ecoregionalisation of the Indian Subantarctic,” is
The PHOCIS project, “Pelagic High Seas Ocean Ecoregionalisation of the Indian Subantarctic,” is
a scientific initiative focused on dividing the open ocean waters around the Indian subantarctic
region into distinct ecological zones based on their unique marine life and environmental
conditions, with the primary goal of identifying and protecting critical conservation areas within
the subantarctic high seas. The integrated ocean management process will encompass the high
seas within 20°E to 150°E and from 40°S to 60°S. Most of the western area falls within the
CCAMLR boundary whereas the eastern area is outside the CCAMLR boundary.
The main objectives for the Cape Town workshop will be for participants to present and discuss
progress on all PHOCIS work packages, but in particular to advance WP4 on Integrated Ocean
Management, and WP5 on Research and Monitoring. Reports generated will be presented to
CCAMLR via the Scientific Committee and its Working Groups.
PHOCIS is structured into 6 WPs (Work Packages), which are further subdivided into sub-WPs:
WP1 Pelagic ecoregionalisation
WP1.1 Geography
WP1.2 Pelagic oceanographic regions
WP1.3 Plankton and pelagic fish spatial distributions
WP1.4 Seabird and marine mammal distributions
WP1.5 Pelagic ecoregionalisation synthesis
WP2 Connectivity between ecoregions
WP3 Historical and forecasting trends
WP4 Integrated Ocean Management
WP4.1 List of conservation objectives
WP4.2 Human impacts
WP4.3 Systematic Conservation Planning
WP4.4 Legal framework
WP5 Research and Monitoring
WP6 Education and knowledge dissemination
Since its inception meeting in 2019 in Cape Town, PHOCIS has been holding workshops on an
annual basis, either online, in-person, or hybrid.
For more info, contact:
Azwianewi Makhado (amakhado@dffe.gov.za) or
Philippe Koubbi (philippe.koubbi@sorbonne-universite.fr)

by Ria Olivier | Aug 11, 2025 | International Days, Marine Protected Area, Microbiology, Research, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean
 Every year on 11 August, World Krill Day draws global attention to the small but mighty Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba)—a cornerstone of the Southern Ocean ecosystem. For decades, the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP) has played a role in advancing krill research, from early expeditions that mapped their distribution and seasonal abundance, to long-term monitoring of how environmental change impacts their population dynamics. Historical studies conducted on board research vessels such as the SA Agulhas have built a foundation of knowledge on krill biology, diet, and role in supporting predators like penguins, seals, and whales. These efforts have helped inform sustainable fishing guidelines and contributed to international collaborations through the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR).
Every year on 11 August, World Krill Day draws global attention to the small but mighty Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba)—a cornerstone of the Southern Ocean ecosystem. For decades, the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP) has played a role in advancing krill research, from early expeditions that mapped their distribution and seasonal abundance, to long-term monitoring of how environmental change impacts their population dynamics. Historical studies conducted on board research vessels such as the SA Agulhas have built a foundation of knowledge on krill biology, diet, and role in supporting predators like penguins, seals, and whales. These efforts have helped inform sustainable fishing guidelines and contributed to international collaborations through the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR).
Today, SANAP’s scientists continue to track krill populations using modern acoustic survey techniques, satellite-linked oceanographic data, and advanced modelling to understand how sea ice shifts and warming waters may affect their future. Current projects explore krill’s role in the carbon cycle and their resilience to environmental stress, while future research aims to integrate genetic studies to assess population connectivity across the Southern Ocean. By combining historical data with cutting-edge science, SANAP is helping to safeguard this keystone species—and, in turn, the health of the entire Antarctic ecosystem.
 On this World Krill Day, we celebrate not just the species itself, but the decades of South African research dedicated to understanding and protecting it.
On this World Krill Day, we celebrate not just the species itself, but the decades of South African research dedicated to understanding and protecting it.
Documents and references available on ALSA Repository

 Honouring Outstanding Contributions
Honouring Outstanding Contributions


 After more than a year on the remote and rugged shores of Gough Island, the Gough 70 Overwintering Team has safely arrived back in Cape Town today — marking the end of another remarkable chapter in South Africa’s contribution to global environmental and climate research.
After more than a year on the remote and rugged shores of Gough Island, the Gough 70 Overwintering Team has safely arrived back in Cape Town today — marking the end of another remarkable chapter in South Africa’s contribution to global environmental and climate research.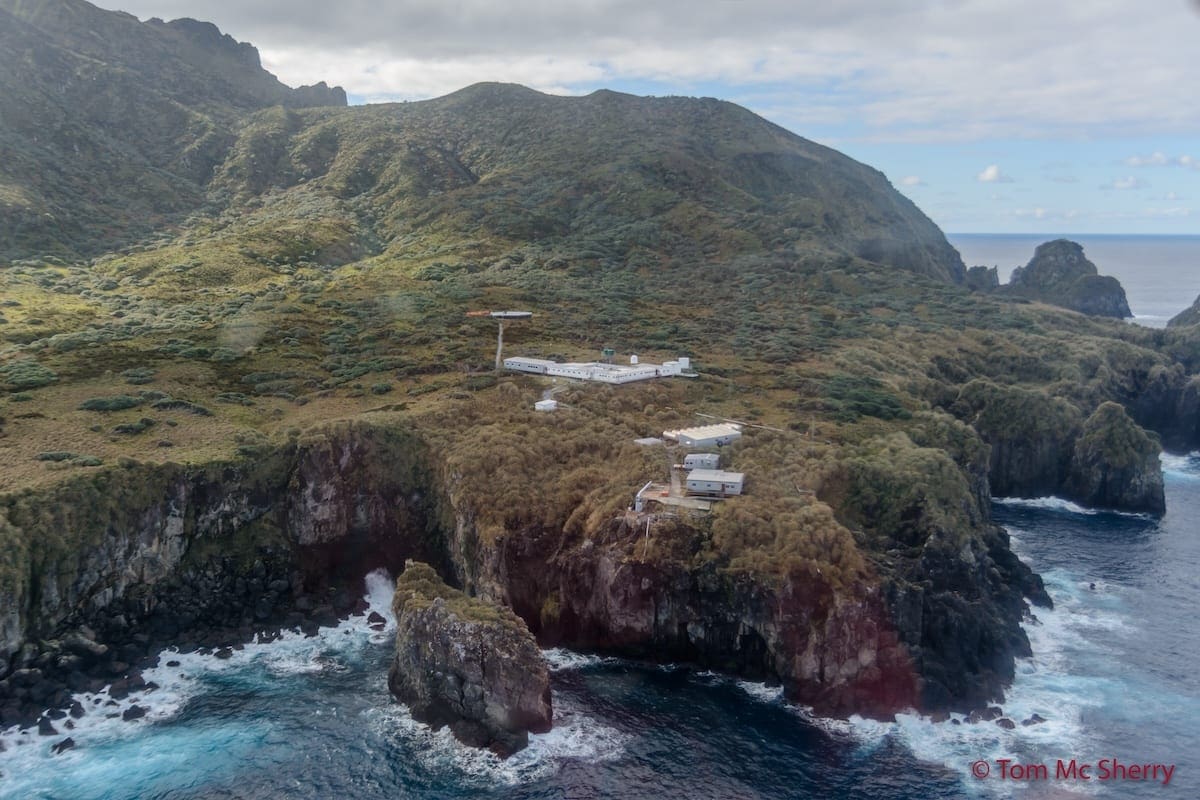 The team has spent the past year maintaining and operating the South African weather and research station on Gough Island, one of the most isolated and scientifically significant islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. Their work forms a vital part of the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), contributing to international understanding of climate systems, ocean–atmosphere interactions, and biodiversity conservation in one of the world’s most pristine environments. Throughout their 13-month stay, the Gough 70 team challenged weather conditions, isolation, and logistical difficulties — yet continued to deliver crucial meteorological observations and research support. Their dedication and resilience embody the true spirit of the SANAP community.
The team has spent the past year maintaining and operating the South African weather and research station on Gough Island, one of the most isolated and scientifically significant islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. Their work forms a vital part of the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), contributing to international understanding of climate systems, ocean–atmosphere interactions, and biodiversity conservation in one of the world’s most pristine environments. Throughout their 13-month stay, the Gough 70 team challenged weather conditions, isolation, and logistical difficulties — yet continued to deliver crucial meteorological observations and research support. Their dedication and resilience embody the true spirit of the SANAP community.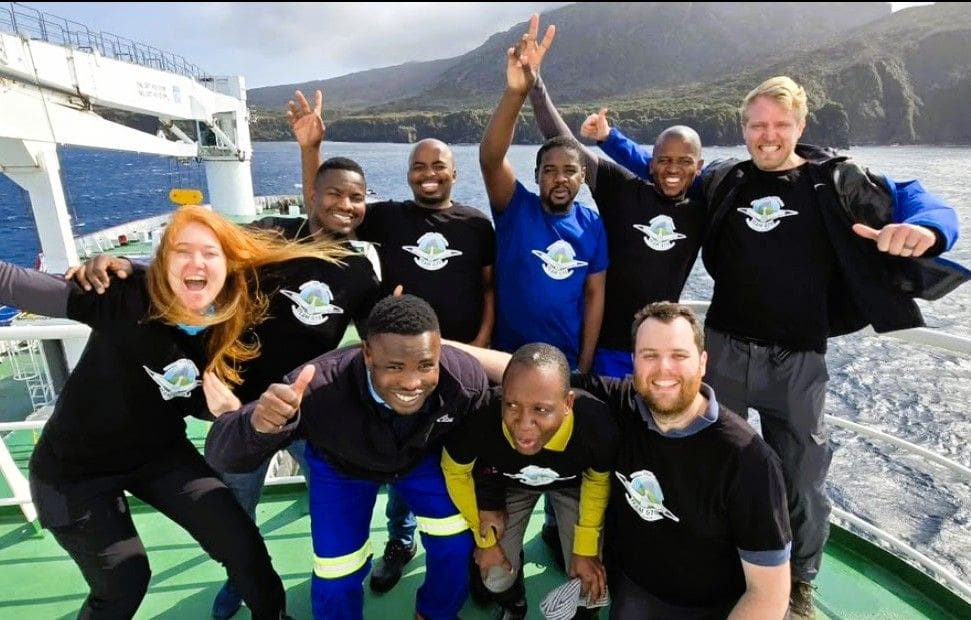 We extend a heartfelt welcome home to each member of the team and express our thanks for their commitment and hard work. Their efforts not only uphold South Africa’s legacy of excellence in polar and sub-Antarctic research but also ensure that critical data continues to support global scientific collaboration. (above taken when arriving at Gough Island in 2024)
We extend a heartfelt welcome home to each member of the team and express our thanks for their commitment and hard work. Their efforts not only uphold South Africa’s legacy of excellence in polar and sub-Antarctic research but also ensure that critical data continues to support global scientific collaboration. (above taken when arriving at Gough Island in 2024)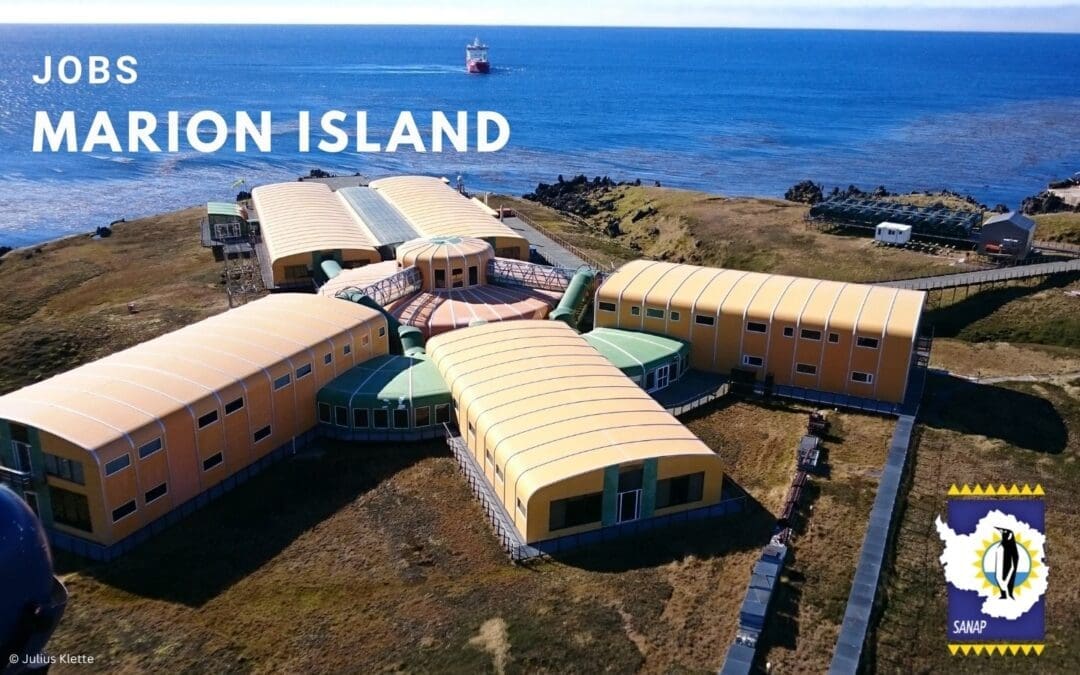


 The PHOCIS project, “Pelagic High Seas Ocean Ecoregionalisation of the Indian Subantarctic,” is
The PHOCIS project, “Pelagic High Seas Ocean Ecoregionalisation of the Indian Subantarctic,” is
 Every year on 11 August,
Every year on 11 August, 




