
by Ria Olivier | Jun 16, 2022 | Announcement, Antarctica, Environment, Gateway cities, Important Dates, News, Women in Science

Youth Day 2022 Theme: Promoting sustainable livelihoods and resilience of young people for a better tomorrow.
The call to action will be for youth to forge resilience and pursue opportunities for a sustainable livelihood, today and in the future (South African Government).

Rudzani Silima, a South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP) graduate, is one of the founding members of the Antarctic Youth Coalition. She is a custodian for South Africa’s gateway city to Antarctica (Cape Town) and “advocating for Antarctica’s future, by promoting sustainable communities and connected urban identities” (AYC).
The five gateway cities to Antarctica:
- Cape Town (South Africa)
- Hobart (Australia)
- Christchurch (New Zealand)
- Punta Arenas (Chile)
- Ushuaia (Argentina)
Who is the Antarctic Youth Coalition?
How did Rudzani become one of the founding members?
Want to know more about Rudzi? Click here!
The Antarctic Youth Coalition is an initiative of the Project: Antarctic cities and the global commons: Rethinking the Gateways.
Read more about the Antarctic Cities Project
Anche Louw, Antarctic Legacy of South Africa, 16 June 2022.

by Ria Olivier | May 11, 2022 | Announcement, Antarctica, Engineering, Environment, News, Research, SA Agulhas II, SANAP, Southern Ocean
Her lecture title is: What can we learn from the way a ship shudders on an icy wreck hunt.
For more info and a link to the LIVE event, click
here.
S.A. Agulhas II Image Credit: Ken Findlay.
Anche Louw, Antarctic Legacy of South Africa, 11 May 2022

by Ria Olivier | Feb 2, 2022 | Announcement, Environment, Gough Island, News, Newsletters>Gough Island Newsletters, Overwintering Team, Team member
In this edition:

- Meet the 67th Gough Island Overwintering Team
- Prof Marthan Bester writes about Fur Seal pup weighing at Tristan da Cunha Islands (2009 – 2021)
- Read more about the Edinburgh ship – connecting Gough with the mainland
- More about the million breeding pairs of Great Shearwater birds on Gough Island
- Weather data of October, November, and December 2021
- Check out some great social gathering pictures!!
Click here to download this issue!!
Click here to view all The Gough Bunting (Gough Newsletters) available on the ALSA Archive.
Anche Louw, Antarctic Legacy of South Africa, 02 February 2022

by Ria Olivier | Aug 27, 2021 | Environment, Marine Protected Area, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Research, SANAP, Science

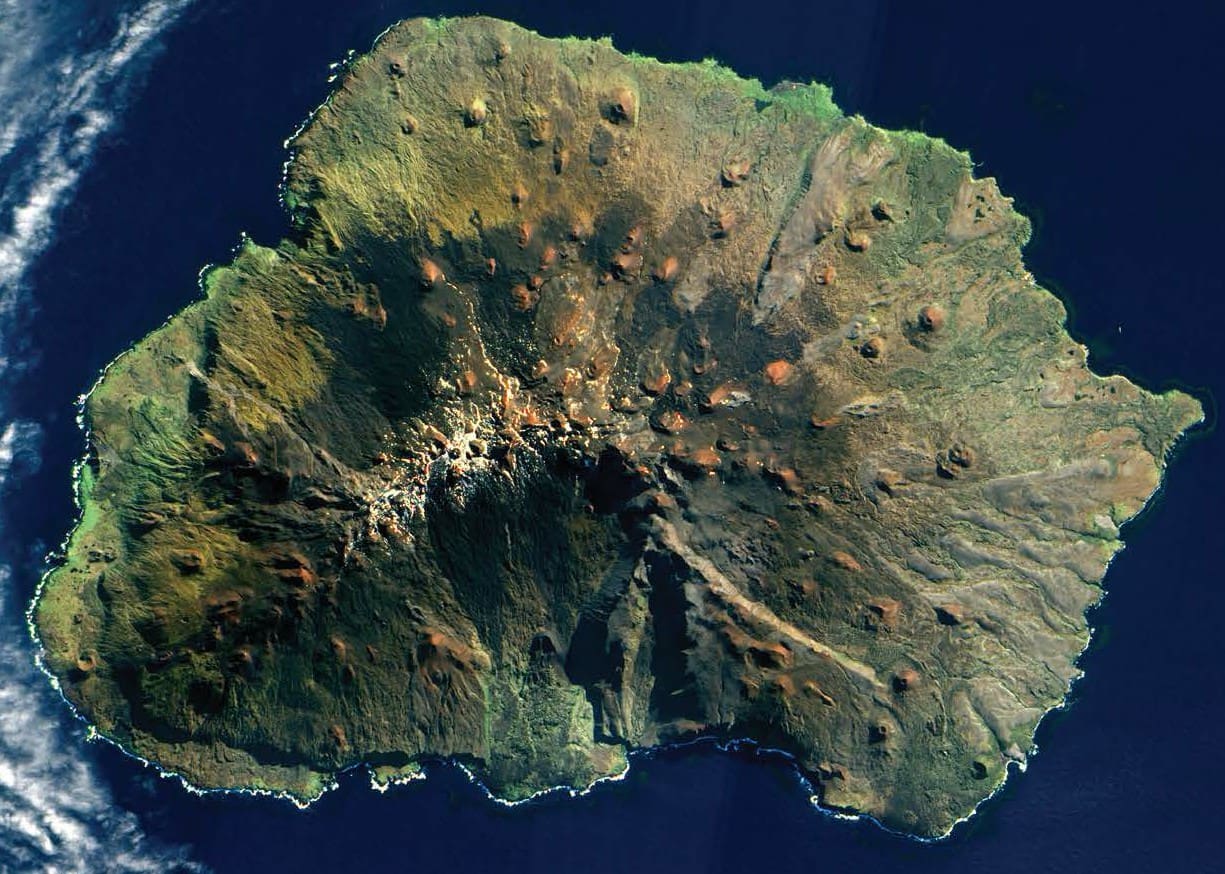
Ecosystem processes are changing worldwide, especially with the impacts of invasive species being exacerbated by climate change.  This is particularly obvious in the Southern Ocean where a warmer and dryer environment allows the proliferation of species once limited by the cold climate. South African Special Nature Reserve, Marion Island is no exception. A recent proliferation of invasive House Mouse attacks on endangered breeding seabirds suggests a profound alteration of the natural ecosystem. This has led to the planned eradication of mice at Marion Island in winter 2023.
This is particularly obvious in the Southern Ocean where a warmer and dryer environment allows the proliferation of species once limited by the cold climate. South African Special Nature Reserve, Marion Island is no exception. A recent proliferation of invasive House Mouse attacks on endangered breeding seabirds suggests a profound alteration of the natural ecosystem. This has led to the planned eradication of mice at Marion Island in winter 2023.

 For the next three years, the new SANAP project co-led by Dr Maëlle Connan (Research Fellow in the Marine Apex Predator Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University) and Prof. Peter Ryan (director of the FitzPatrick Institute of African Ornithology – University of Cape Town) will focus on three data deficient species of avian scavengers: Black-faced Sheathbill, Kelp Gull and Brown Skua.
For the next three years, the new SANAP project co-led by Dr Maëlle Connan (Research Fellow in the Marine Apex Predator Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University) and Prof. Peter Ryan (director of the FitzPatrick Institute of African Ornithology – University of Cape Town) will focus on three data deficient species of avian scavengers: Black-faced Sheathbill, Kelp Gull and Brown Skua.
By focusing on these three species and some of their prey, the project intends first to fill identified scientific gaps that are crucial for best planning of the mouse eradication. Second, these three scavengers will be used as indicators of recovery of the terrestrial ecosystem post-eradication by establishing baselines for the scavenger guild and their prey against which the impact of a successful mouse eradication can be measured in years to come. (Above: Left – Maelle Connan, Right – Peter Ryan)

 (Above l-r: Sub-Antarctic Skua, Black-Faced Sheathbill)
(Above l-r: Sub-Antarctic Skua, Black-Faced Sheathbill)

(Above: Eleanor Weideman on Marion Island)
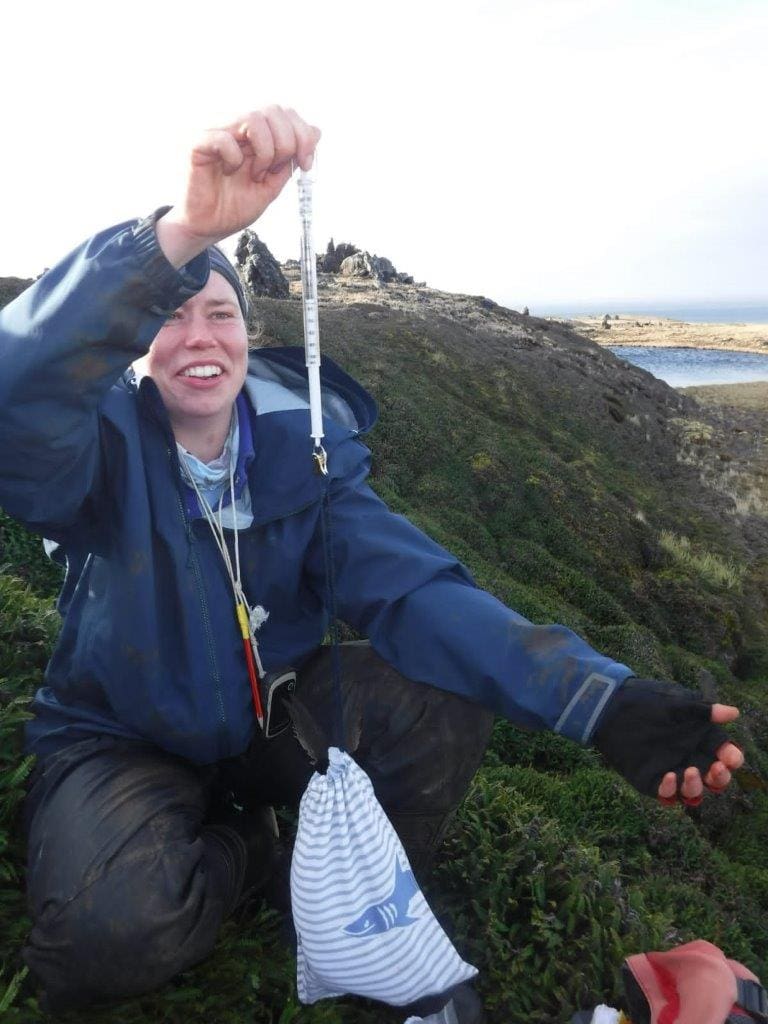
An important aspect of the project will entail conducting regular censuses and seasonal round island counts in addition to behavioural observations of the focal scavenger species. Indeed, the three species to be studied are at the top of the terrestrial food chain, and thus can be used as indicators of recovery of the island biota post-eradication.
 On one hand, Black-faced Sheathbills and Kelp Gulls used to predate on terrestrial invertebrates, at least seasonally, but this behaviour has decreased in sheathbills as invertebrate populations have collapsed through mouse predation. There are no recent data for Kelp Gulls. On the other hand, many pairs of Brown Skuas predate mainly on burrowing petrels, thus will inform on the recovery of these nocturnal species from mouse predation. The skua data will be complemented by the implementation of an automated acoustic monitoring to detect the presence and coarse distribution of the most elusive and cryptic nocturnal species which are notoriously difficult to study. (Left – Eleanor Weideman in the field on Marion Island.)
On one hand, Black-faced Sheathbills and Kelp Gulls used to predate on terrestrial invertebrates, at least seasonally, but this behaviour has decreased in sheathbills as invertebrate populations have collapsed through mouse predation. There are no recent data for Kelp Gulls. On the other hand, many pairs of Brown Skuas predate mainly on burrowing petrels, thus will inform on the recovery of these nocturnal species from mouse predation. The skua data will be complemented by the implementation of an automated acoustic monitoring to detect the presence and coarse distribution of the most elusive and cryptic nocturnal species which are notoriously difficult to study. (Left – Eleanor Weideman in the field on Marion Island.)
Data obtained during the project will be swiftly shared to the Mouse-Free Marion programme manager Dr Anton Wolfaardt, to ensure updated information is available for the best planning of the mouse eradication.
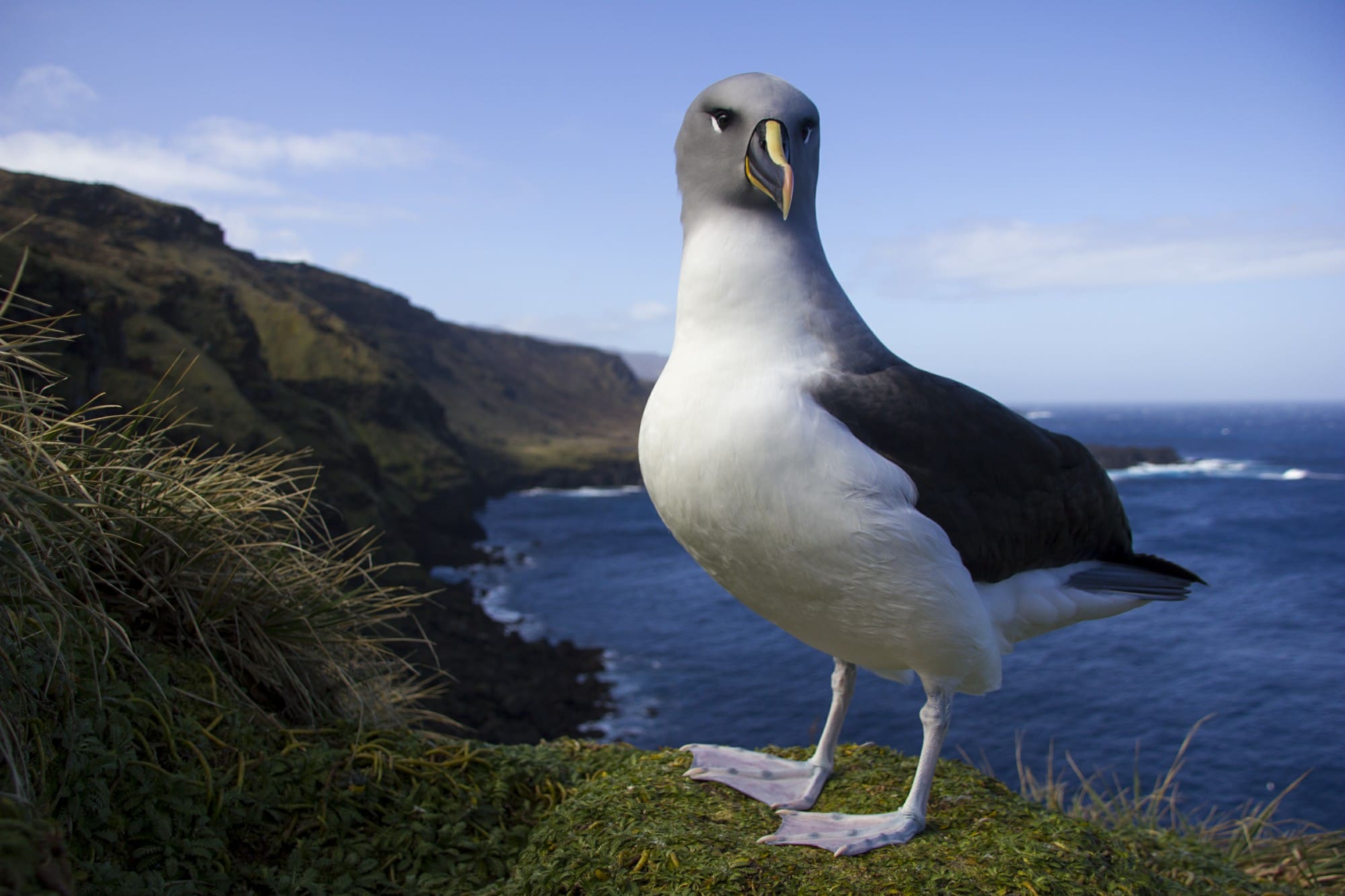
 Cover Image: Sub-Antarctic Skua – photo credit: Maelle Connan
Cover Image: Sub-Antarctic Skua – photo credit: Maelle Connan
Text supplied by Maelle Connan.
Photo Credits: Maelle Connan, Yinhla Shihlomuhe, Isabel Micklem.

by Ria Olivier | Jul 5, 2021 | Biosecurity, Environment, Invasion Biology, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Research, Science


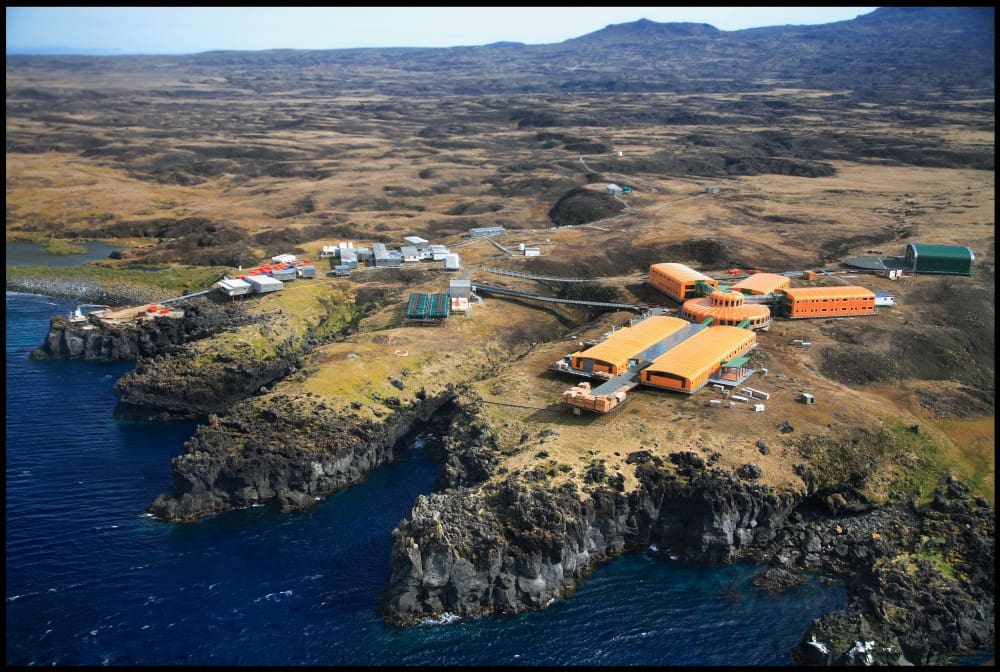
 Marion Island (29 000 hectares) and Prince Edward (4500 hectares), collectively known as the Prince Edward Islands (PEIs) were annexed by South Africa in December 1947 and January 1948, respectively. Since then, South Africa has maintained a research and weather station on Marion Island, Prince Edward remains uninhabited. The PEIs were declared a Special Nature Reserve in 1995, a Ramsar Wetland Site of International Importance in 2007 and the surrounding waters a Marine Protected Area in 2009. The islands, governed by a suite of national environmental legislation under the Prince Edward Islands Management Plan (which includes a plan for the control and eradication of invasive alien species), are managed by the Oceans and Coasts Branch of the Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE) as the designated Management Authority under the National Environmental Management Protected Areas Act 57 of 2003.
Marion Island (29 000 hectares) and Prince Edward (4500 hectares), collectively known as the Prince Edward Islands (PEIs) were annexed by South Africa in December 1947 and January 1948, respectively. Since then, South Africa has maintained a research and weather station on Marion Island, Prince Edward remains uninhabited. The PEIs were declared a Special Nature Reserve in 1995, a Ramsar Wetland Site of International Importance in 2007 and the surrounding waters a Marine Protected Area in 2009. The islands, governed by a suite of national environmental legislation under the Prince Edward Islands Management Plan (which includes a plan for the control and eradication of invasive alien species), are managed by the Oceans and Coasts Branch of the Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE) as the designated Management Authority under the National Environmental Management Protected Areas Act 57 of 2003.


 The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.
The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.
 With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)
With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)
Marion Island supports some 25% of the world’s breeding population of Wandering Diomedea exulans, 12% of Sooty Phoebetria fusca and 7% of Grey-headed Thalassarche chrysostoma Albatrosses and smaller percentages of Light-mantled Albatrosses P. palpebrata and Grey Petrels Procellaria cinerea. It is clear something needs to be done or the severe impact of the mice could result in critical impacts on global populations and in the extirpation of up to 18 of the 27 bird species found on Marion within the next 30 to 100 years. (below l-r: Wandering Albatross, Sooty Albatross and chick, Grey-headed Albatross and chick. (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie)



 In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a Feasibility Study and Risk Assessment, undertaken in 2016 by John Parkes on behalf of BirdLife South Africa (BLSA), indicated that eradication was indeed possible. Also funded by BLSA, Draft Project and Operational Plans to eradicate mice on Marion Island were subsequently developed in 2018 by New Zealand eradication expert, Keith Springer, following an island visit. DFFE has been working closely with the UK’s Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) over the last few years in support of the Gough Island Restoration Programme (GIRP) which aims to eradicate House Mice on Gough during June to September 2021. For more information and the latest updates on the GIRP, please visit: https://www.goughisland.com
In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a Feasibility Study and Risk Assessment, undertaken in 2016 by John Parkes on behalf of BirdLife South Africa (BLSA), indicated that eradication was indeed possible. Also funded by BLSA, Draft Project and Operational Plans to eradicate mice on Marion Island were subsequently developed in 2018 by New Zealand eradication expert, Keith Springer, following an island visit. DFFE has been working closely with the UK’s Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) over the last few years in support of the Gough Island Restoration Programme (GIRP) which aims to eradicate House Mice on Gough during June to September 2021. For more information and the latest updates on the GIRP, please visit: https://www.goughisland.com
On 12 May 2020, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the Mouse-Free Marion (MFM) Project was signed between DFFE and BLSA. Subsequently, a MFM Management Committee was established to initiate the development of the project and the two MoU partners are now working closely, together with various experts and institutions (including those involved with successful operations on other islands), on the detailed planning on all operational aspects required for the execution of this complex and costly project.


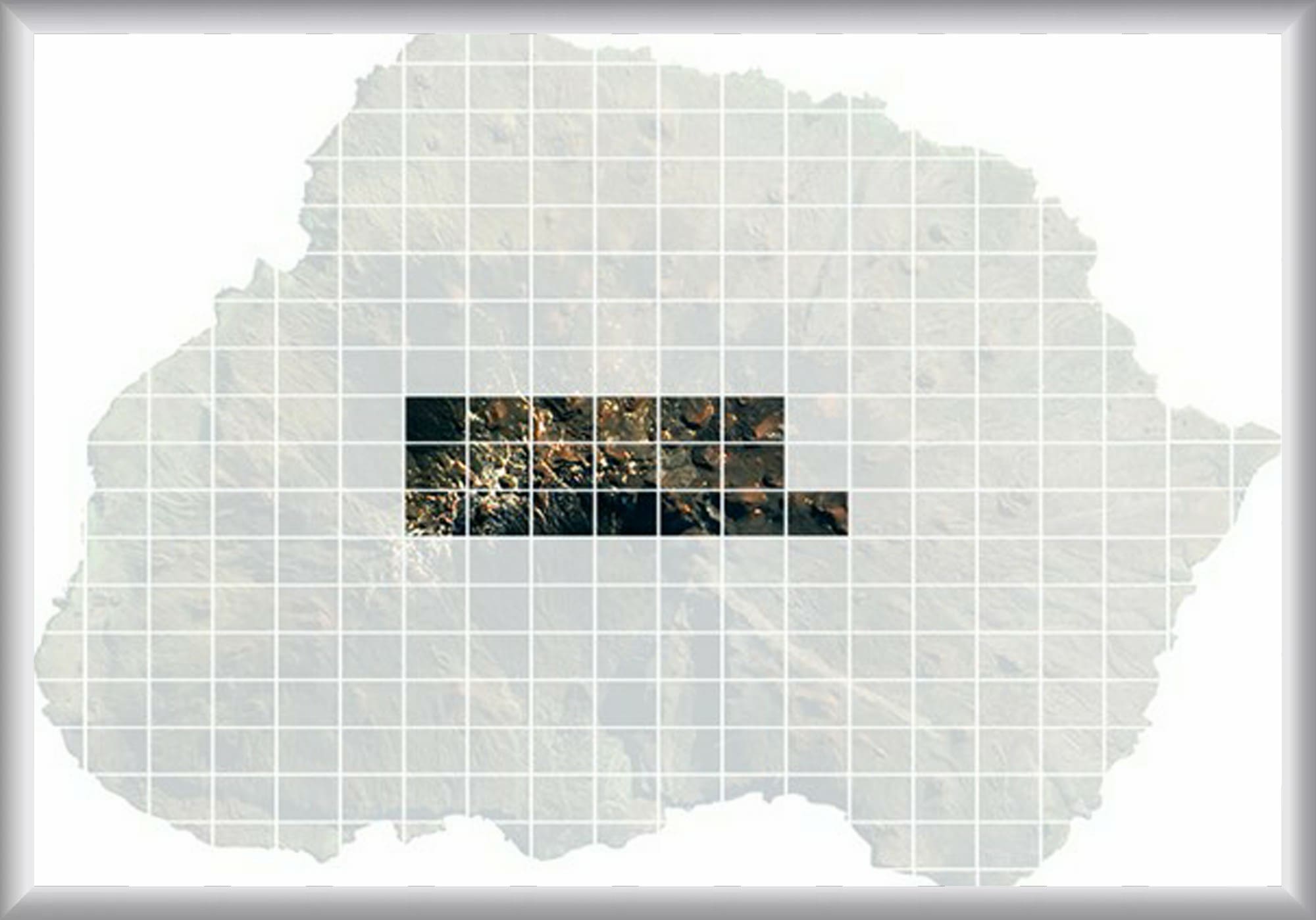
The MFM Project will make use of internationally agreed best-practice approaches to eradicate mice from the island. The Feasibility Study and draft Project and Operational Plans highlight that the only methodology offering any chance of success on an island of the size and topography of Marion Island is aerial spreading of bait containing a rodenticide with a proven capacity to eradicate mice.  The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the base and other infrastructure on the island. If a single pregnant female is not targeted, it could result in the failure of the entire operation, but if it works, Marion Island will be by far the largest island in the world from which House Mice have successfully been eradicated.
The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the base and other infrastructure on the island. If a single pregnant female is not targeted, it could result in the failure of the entire operation, but if it works, Marion Island will be by far the largest island in the world from which House Mice have successfully been eradicated.
Time window trade-offs have been assessed and it has been determined that winter (April/May – August/September) is the optimal period in which to implement an eradication operation. This is the non-breeding period for mice at Marion, when their population size is low and natural food resources are minimal, rendering bait more attractive. A winter-baiting operation also reduces the risks to non-target seabird species on the island, as many are not resident on the island during the winter months.
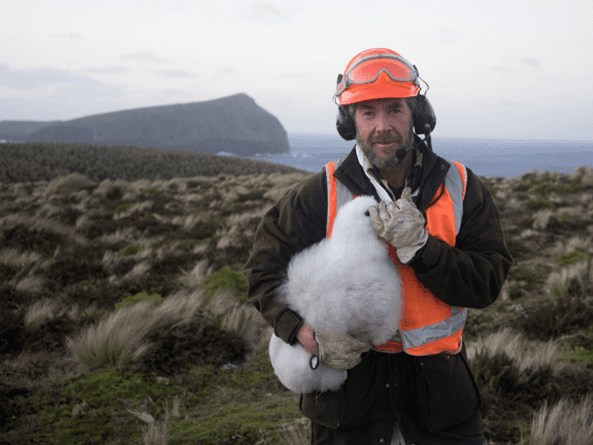
Currently, the eradication exercise is planned for the austral winter of 2023 and, to review and update the Project and Operational Plans, a Project Manager (Dr Anton Wolfaardt – photo left) and an Operations Manager (Mr Keith Springer – photo right) have been appointed.


 A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘Sponsor a Hectare’ (which is currently standing at just over R2 million), please visit http://www.mousefreemarion.org.za
A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘Sponsor a Hectare’ (which is currently standing at just over R2 million), please visit http://www.mousefreemarion.org.za
Text compiled by Carol Jacobs - Directorate: Biosecurity (DFFE)
Images from Marion Mouse Free Project, Stefan Schoombie,
FitzPatrick Institute and Antarctic Legacy of South Africa digital archive.
Cover Image: Otto Whitehead
,

by Ria Olivier | Jun 5, 2021 | Environment, International Days
 World Environment Day 2021 will see the launch of the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration:
World Environment Day 2021 will see the launch of the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration:
“TEN MORE YEARS TO RESTORE THE PLANET”

 With the celebration of Environment Day on 5 June 2021 with the theme: “Reimagine, Recreate, Restore” we highlight the objectives of the South African National Antarctic Programme(SANAP). SANAP plays a crucial role in conserving this living laboratory. Studies done in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic are inextricably linked to our understanding of the entire Earth. SANAP recognises the global and national importance of safeguarding the environment of the Antarctic and Southern Ocean and protecting the integrity of ecosystems, both marine and terrestrial, in the region. The programme takes cognisance of the presence of natural resources (both renewable and non-renewable) and the increased interest in their possible utilisation (both consumptive and non-consumptive).
With the celebration of Environment Day on 5 June 2021 with the theme: “Reimagine, Recreate, Restore” we highlight the objectives of the South African National Antarctic Programme(SANAP). SANAP plays a crucial role in conserving this living laboratory. Studies done in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic are inextricably linked to our understanding of the entire Earth. SANAP recognises the global and national importance of safeguarding the environment of the Antarctic and Southern Ocean and protecting the integrity of ecosystems, both marine and terrestrial, in the region. The programme takes cognisance of the presence of natural resources (both renewable and non-renewable) and the increased interest in their possible utilisation (both consumptive and non-consumptive).

 Conservation challenges on the Prince Edward Islands (South African most southern Islands): “.. increasingly stringent conservation measures mean that the Prince Edward Islands and the surrounding oceans face far fewer conservation challenges than do most other island groups. The challenges that do remain and the natural laboratory setting that the islands provide for understanding ecological processes, give a means for researchers to assess how these challenges can be forecast, managed, and overcome. Indeed, today, the Prince Edward Islands and their surrounding oceans are largely managed for conservation and for science.” – Marion & Prince Edward Island; Africa’s Southern Islands by A Terauds, J Cooper, S Chown and P Ryan.
Conservation challenges on the Prince Edward Islands (South African most southern Islands): “.. increasingly stringent conservation measures mean that the Prince Edward Islands and the surrounding oceans face far fewer conservation challenges than do most other island groups. The challenges that do remain and the natural laboratory setting that the islands provide for understanding ecological processes, give a means for researchers to assess how these challenges can be forecast, managed, and overcome. Indeed, today, the Prince Edward Islands and their surrounding oceans are largely managed for conservation and for science.” – Marion & Prince Edward Island; Africa’s Southern Islands by A Terauds, J Cooper, S Chown and P Ryan.
 “There has never been a more urgent need to revive damaged ecosystems than now. Ecosystems support all life on Earth. The healthier our ecosystems are, the healthier the planet – and its people. The UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration aims to prevent, halt and reverse the degradation of ecosystems on every continent and in every ocean.”
“There has never been a more urgent need to revive damaged ecosystems than now. Ecosystems support all life on Earth. The healthier our ecosystems are, the healthier the planet – and its people. The UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration aims to prevent, halt and reverse the degradation of ecosystems on every continent and in every ocean.”
Visit the Mouse-Free Marion t and the Gough island Restoration websites – with the aim to restore the environment.
 TOGETHER WE CAN BE #GENERATIONRESTORATION
TOGETHER WE CAN BE #GENERATIONRESTORATION
 (Images above – Tom Mcsherry, available on ALSA Archive)
(Images above – Tom Mcsherry, available on ALSA Archive)
 South Africa’s Department of Fisheries, Forestry and the Environment (DFFE) South Africa celebrates World Environment Day. The Minister of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment, Ms Barbara Creecy will mark this year’s World Environment Day by reflecting on 25 years of DFFE/ United Nations Development Programme cooperation, on Saturday 5 June 2021.
South Africa’s Department of Fisheries, Forestry and the Environment (DFFE) South Africa celebrates World Environment Day. The Minister of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment, Ms Barbara Creecy will mark this year’s World Environment Day by reflecting on 25 years of DFFE/ United Nations Development Programme cooperation, on Saturday 5 June 2021.










 This is particularly obvious in the Southern Ocean where a warmer and dryer environment allows the proliferation of species once limited by the cold climate. South African
This is particularly obvious in the Southern Ocean where a warmer and dryer environment allows the proliferation of species once limited by the cold climate. South African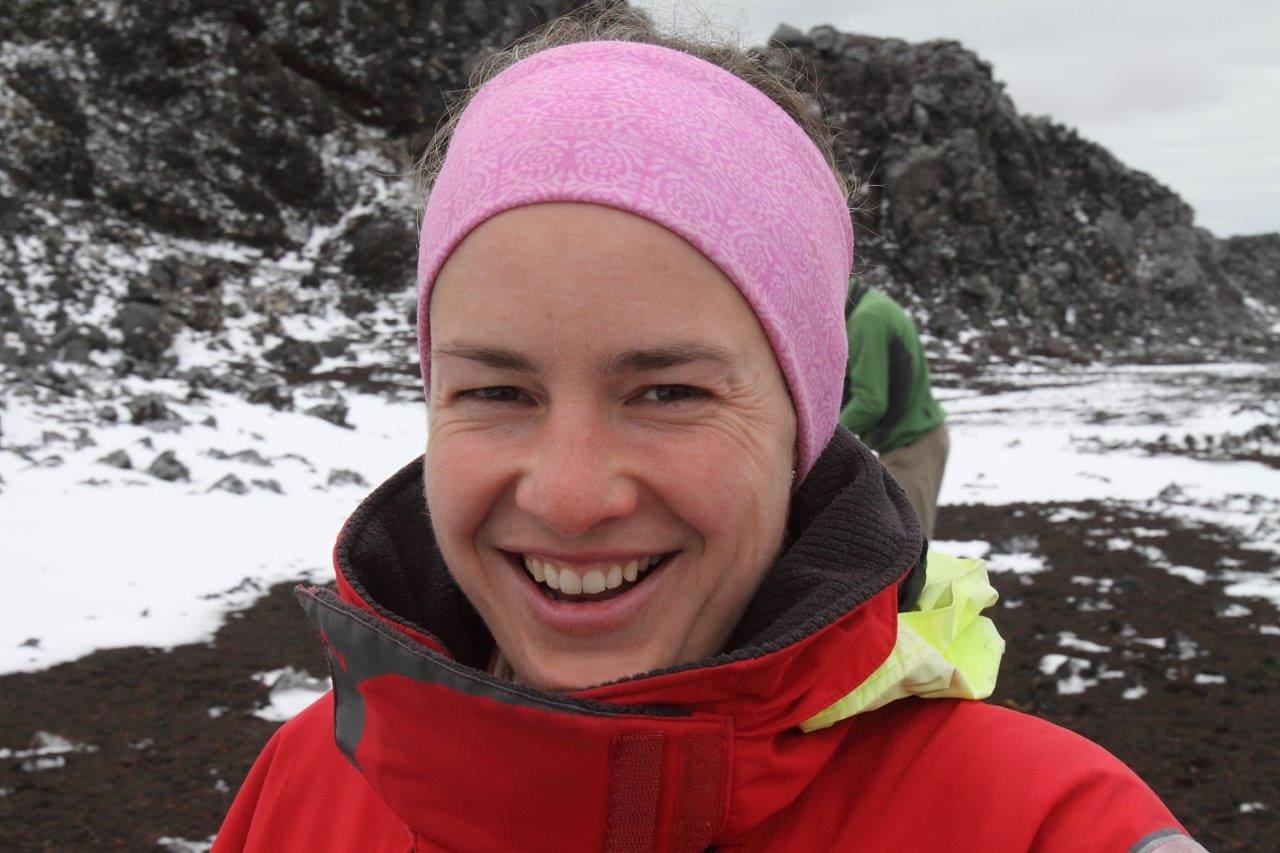 
 For the next three years, the new SANAP project co-led by Dr Maëlle Connan (Research Fellow in the
For the next three years, the new SANAP project co-led by Dr Maëlle Connan (Research Fellow in the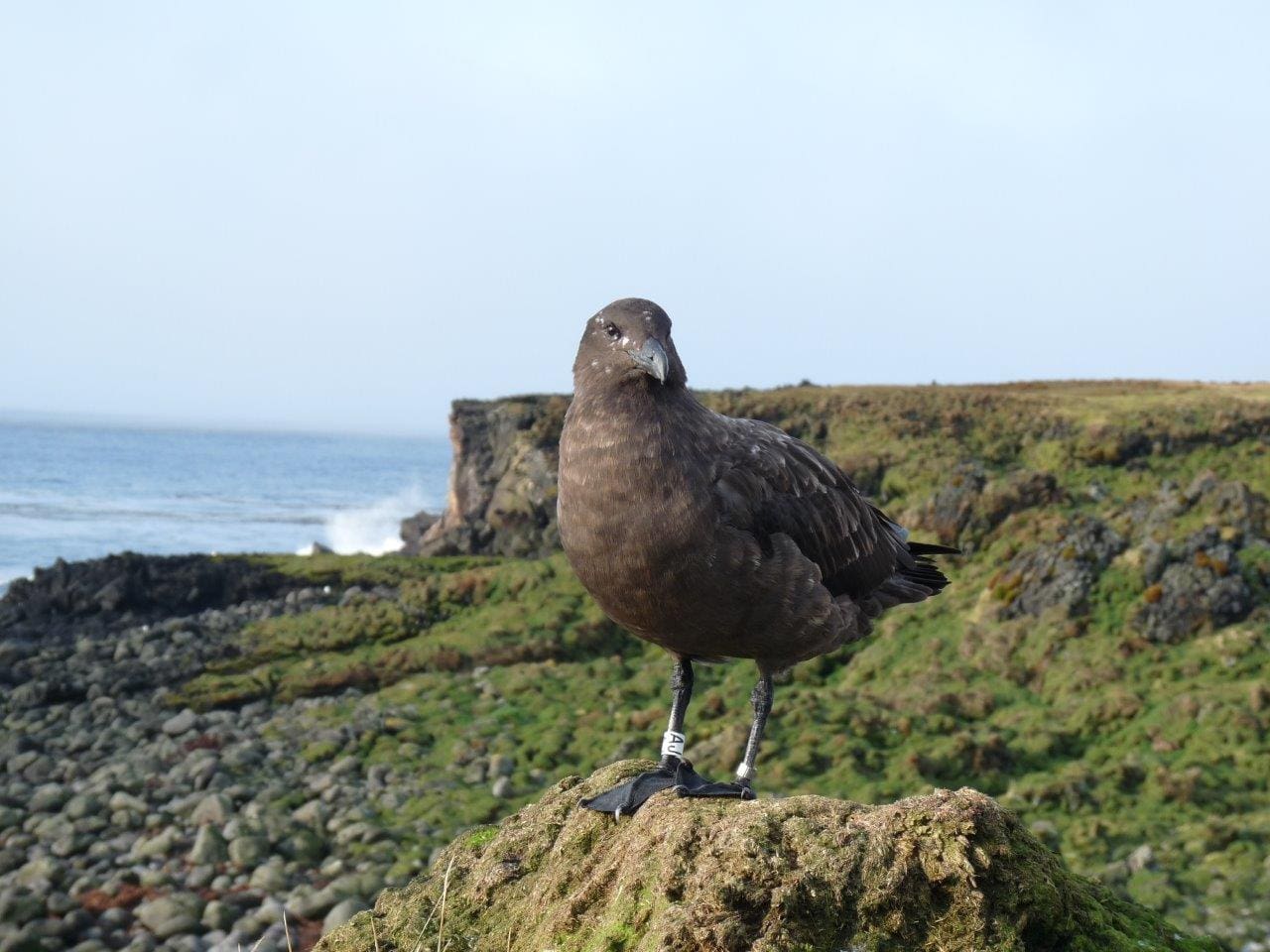 
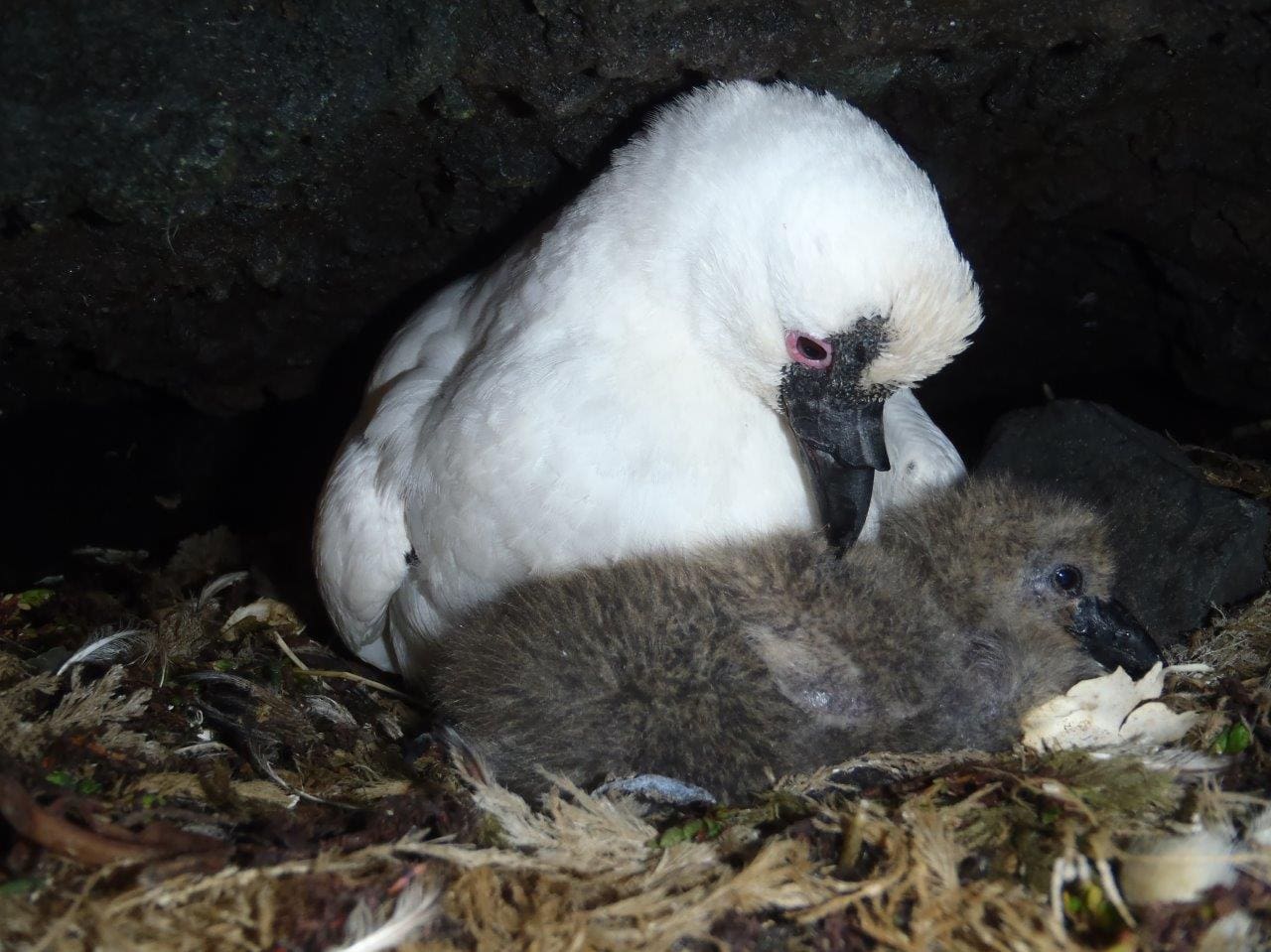 (Above l-r: Sub-Antarctic Skua, Black-Faced Sheathbill)
(Above l-r: Sub-Antarctic Skua, Black-Faced Sheathbill)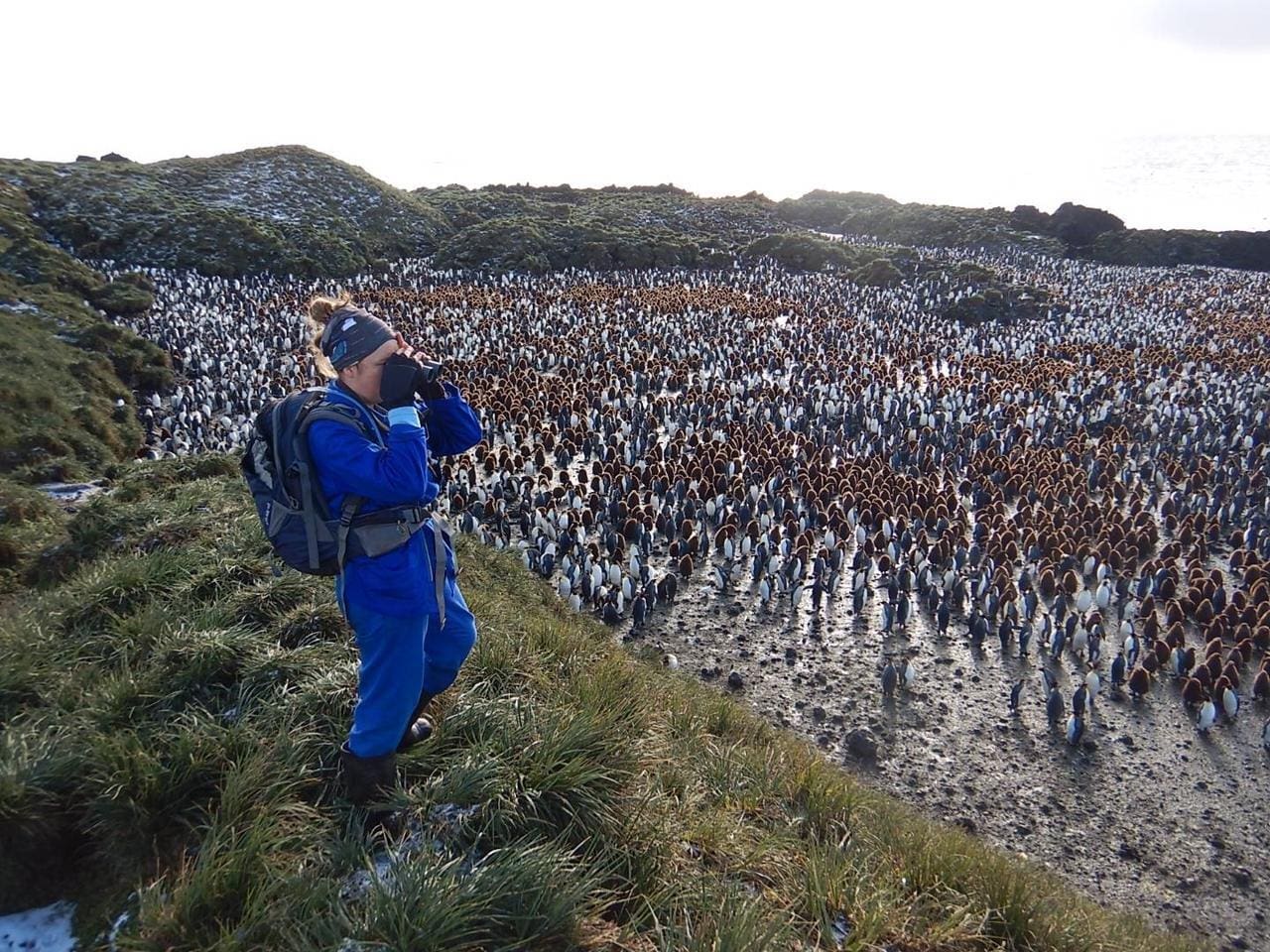
 On one hand, Black-faced Sheathbills and Kelp Gulls used to predate on terrestrial invertebrates, at least seasonally, but this behaviour has decreased in sheathbills as invertebrate populations have collapsed through mouse predation. There are no recent data for Kelp Gulls. On the other hand, many pairs of Brown Skuas predate mainly on burrowing petrels, thus will inform on the recovery of these nocturnal species from mouse predation. The skua data will be complemented by the implementation of an automated acoustic monitoring to detect the presence and coarse distribution of the most elusive and cryptic nocturnal species which are notoriously difficult to study. (Left – Eleanor Weideman in the field on Marion Island.)
On one hand, Black-faced Sheathbills and Kelp Gulls used to predate on terrestrial invertebrates, at least seasonally, but this behaviour has decreased in sheathbills as invertebrate populations have collapsed through mouse predation. There are no recent data for Kelp Gulls. On the other hand, many pairs of Brown Skuas predate mainly on burrowing petrels, thus will inform on the recovery of these nocturnal species from mouse predation. The skua data will be complemented by the implementation of an automated acoustic monitoring to detect the presence and coarse distribution of the most elusive and cryptic nocturnal species which are notoriously difficult to study. (Left – Eleanor Weideman in the field on Marion Island.) Cover Image: Sub-Antarctic Skua – photo credit: Maelle Connan
Cover Image: Sub-Antarctic Skua – photo credit: Maelle Connan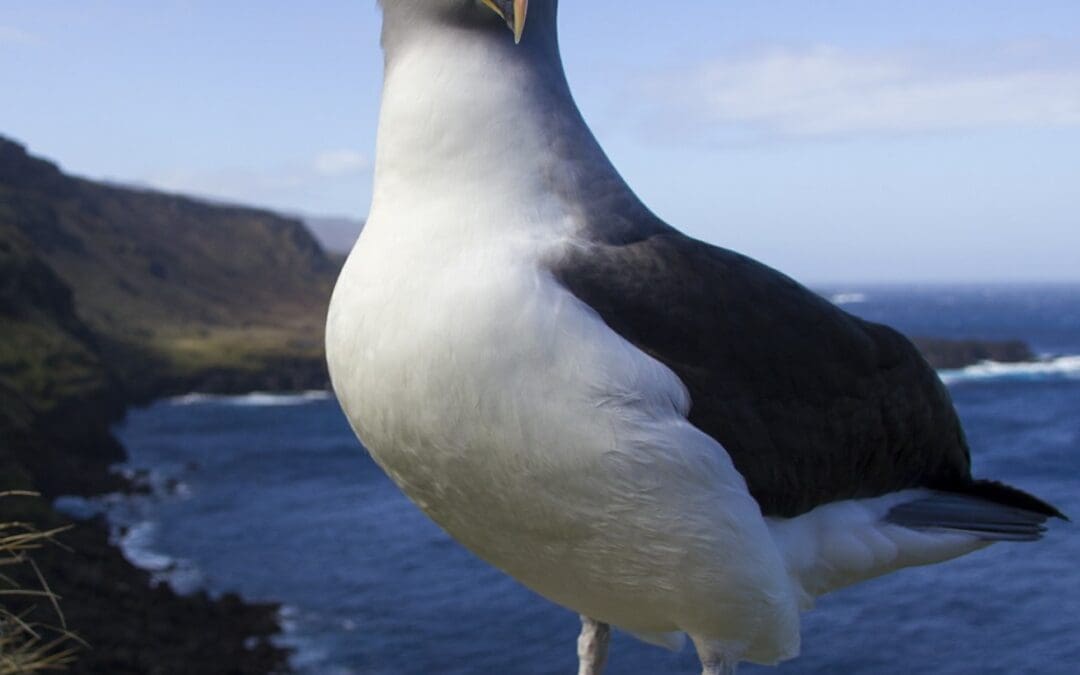
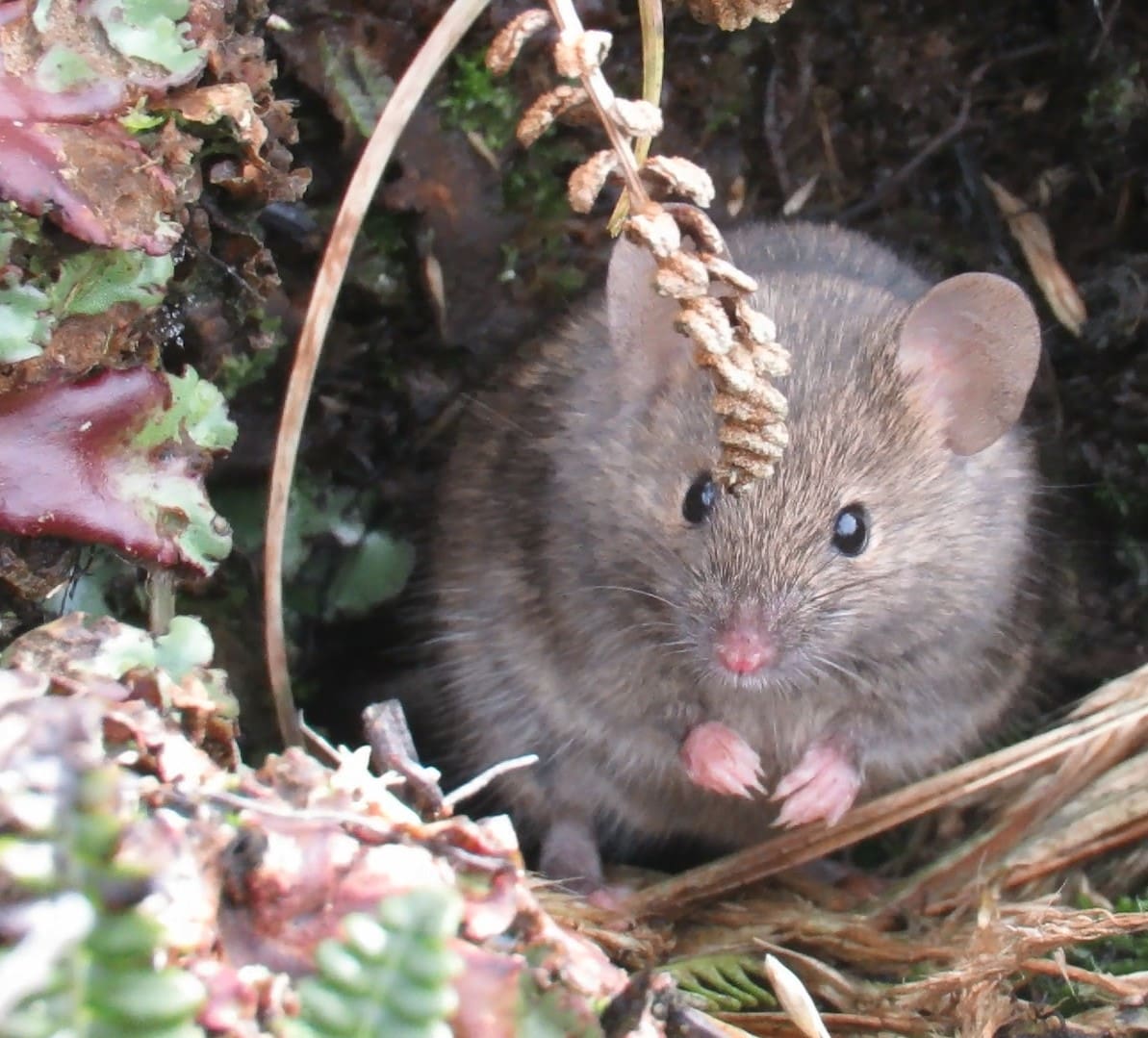
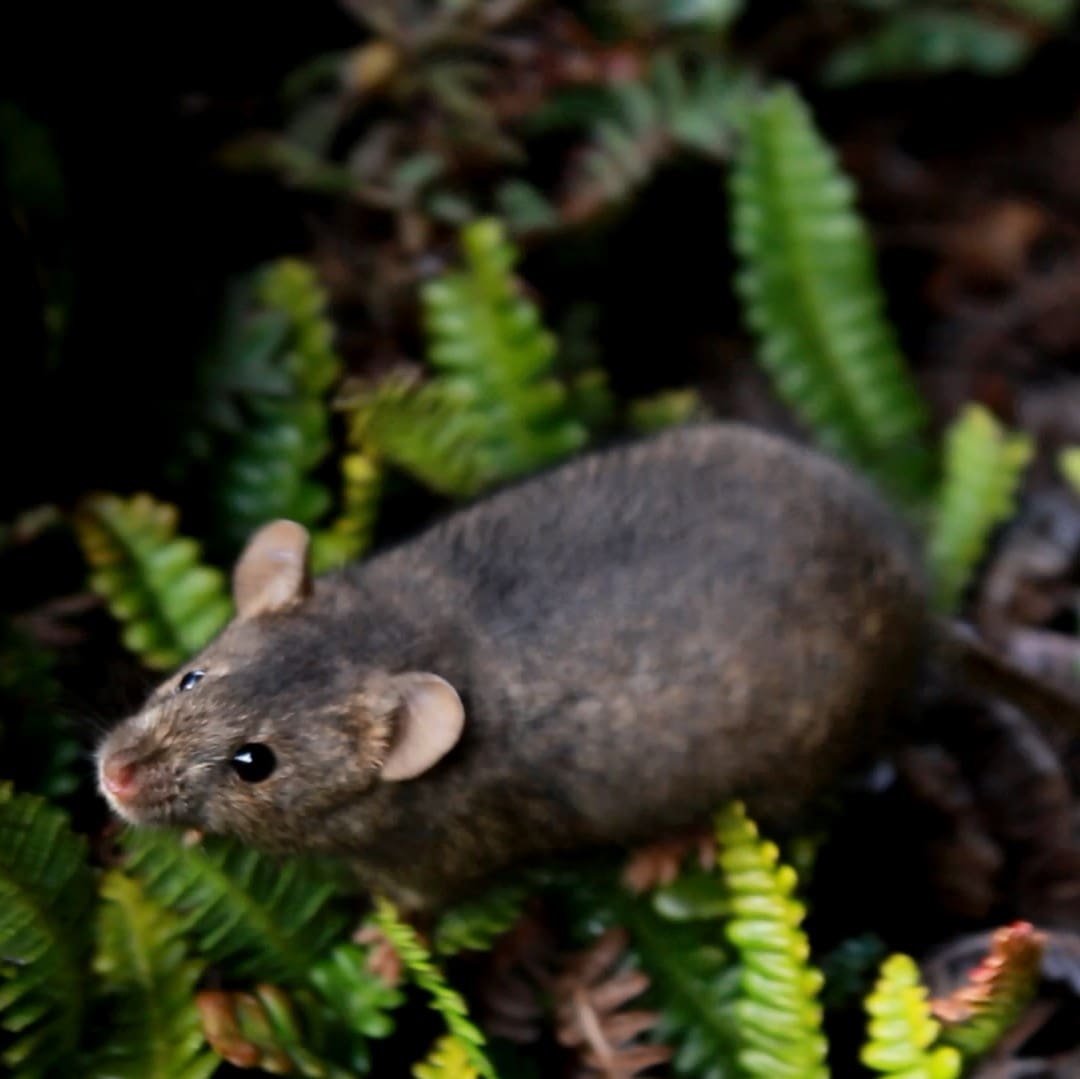
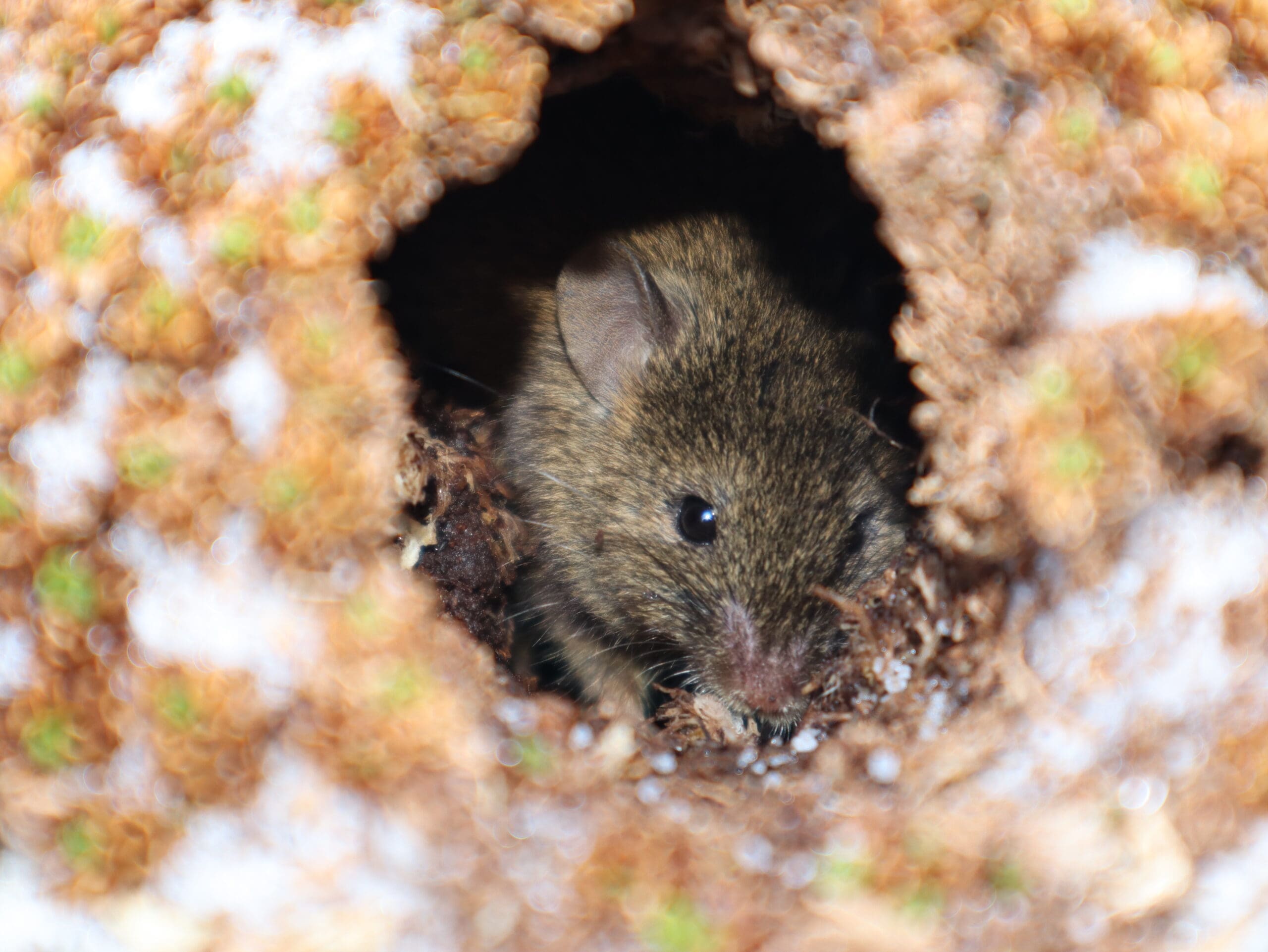


 The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.
The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.  With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)
With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)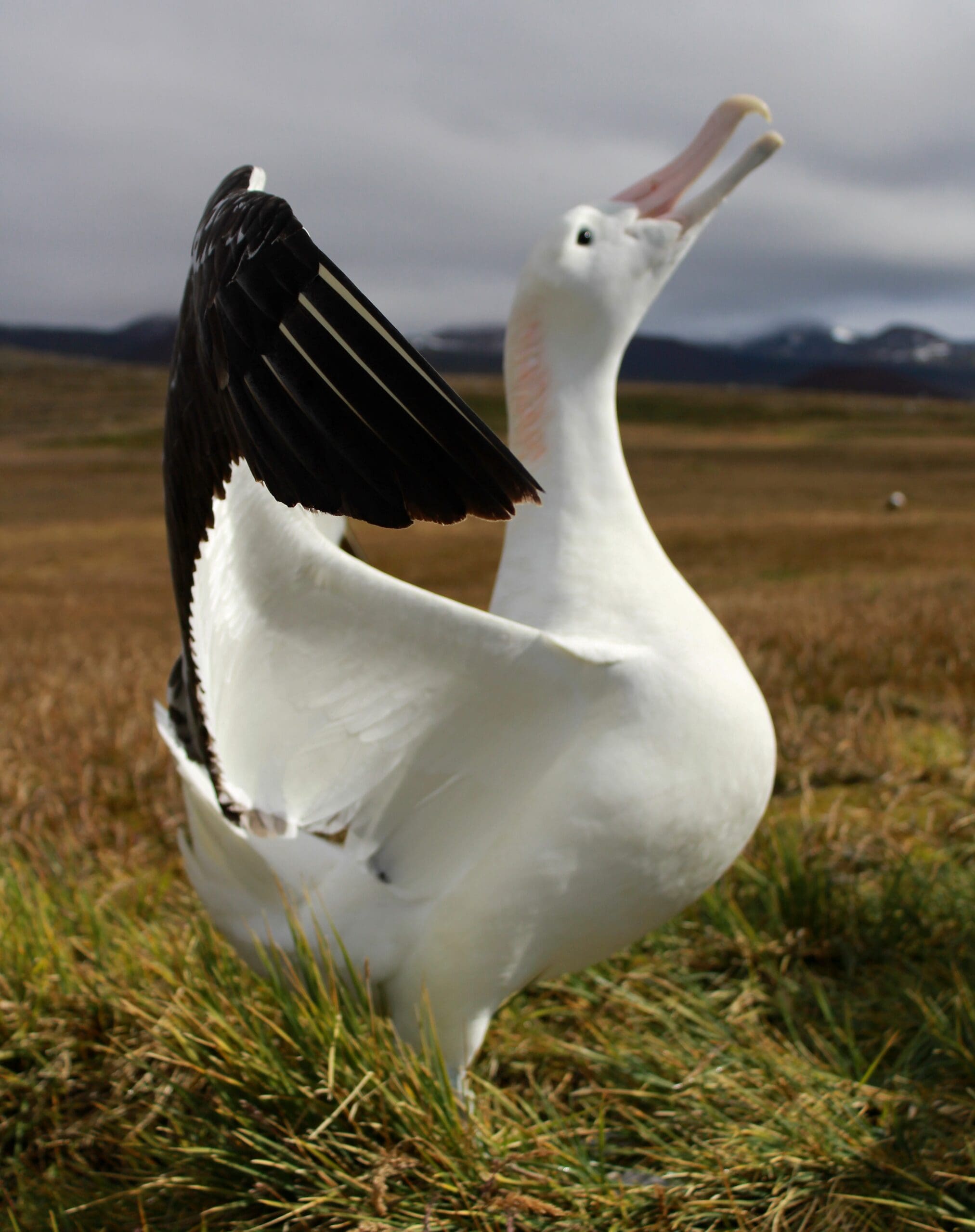


 In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a
In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a 
 The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the
The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the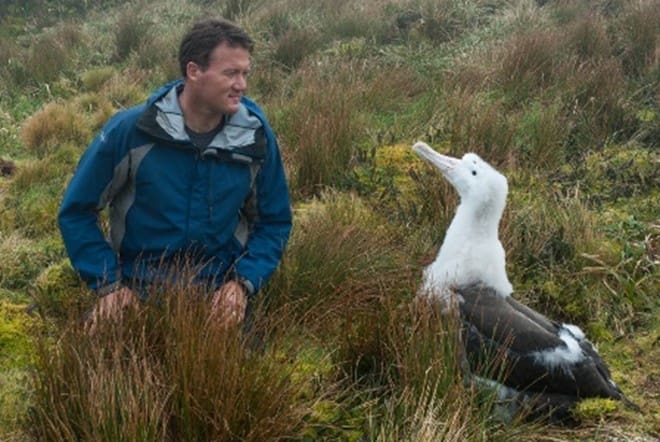 
 A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘
A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘
 World Environment Day 2021 will see the launch of the
World Environment Day 2021 will see the launch of the 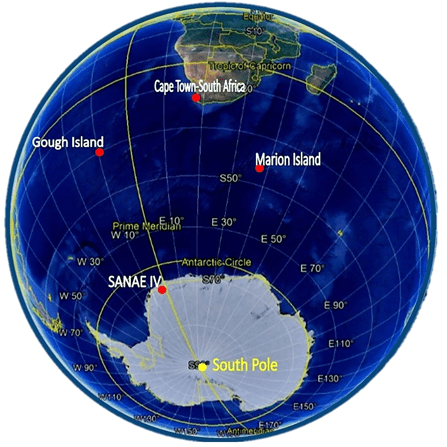
 With the celebration of Environment Day on 5 June 2021 with the theme: “Reimagine, Recreate, Restore” we highlight the objectives of the
With the celebration of Environment Day on 5 June 2021 with the theme: “Reimagine, Recreate, Restore” we highlight the objectives of the 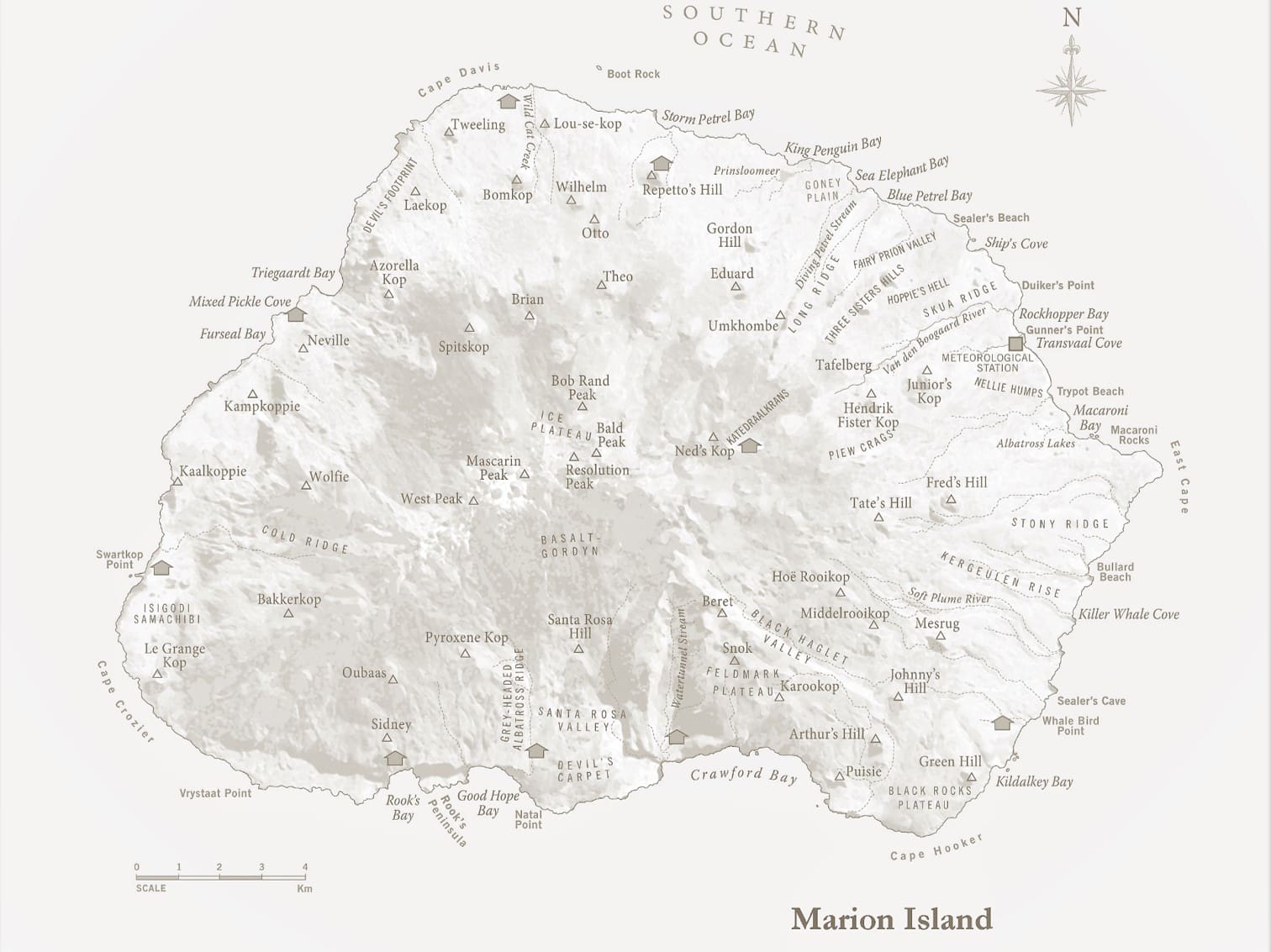
 Conservation challenges on the Prince Edward Islands (South African most southern Islands): “.. increasingly stringent conservation measures mean that the Prince Edward Islands and the surrounding oceans face far fewer conservation challenges than do most other island groups. The challenges that do remain and the natural laboratory setting that the islands provide for understanding ecological processes, give a means for researchers to assess how these challenges can be forecast, managed, and overcome. Indeed, today, the Prince Edward Islands and their surrounding oceans are largely managed for conservation and for science.” – Marion & Prince Edward Island; Africa’s Southern Islands by A Terauds, J Cooper, S Chown and P Ryan.
Conservation challenges on the Prince Edward Islands (South African most southern Islands): “.. increasingly stringent conservation measures mean that the Prince Edward Islands and the surrounding oceans face far fewer conservation challenges than do most other island groups. The challenges that do remain and the natural laboratory setting that the islands provide for understanding ecological processes, give a means for researchers to assess how these challenges can be forecast, managed, and overcome. Indeed, today, the Prince Edward Islands and their surrounding oceans are largely managed for conservation and for science.” – Marion & Prince Edward Island; Africa’s Southern Islands by A Terauds, J Cooper, S Chown and P Ryan.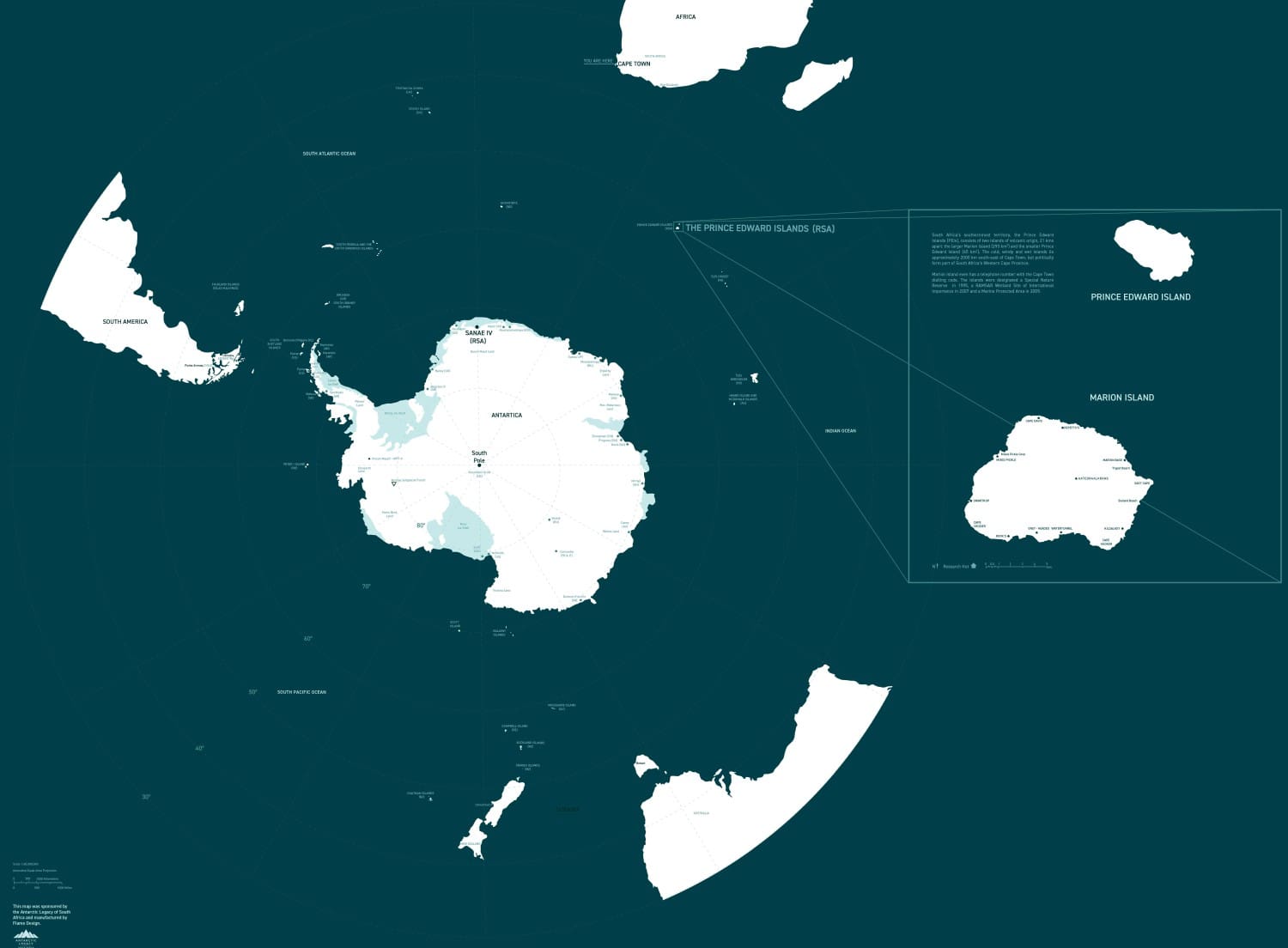 “There has never been a more urgent need to revive damaged ecosystems than now. Ecosystems support all life on Earth. The healthier our ecosystems are, the healthier the planet – and its people. The UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration aims to prevent, halt and reverse the degradation of ecosystems on every continent and in every ocean.”
“There has never been a more urgent need to revive damaged ecosystems than now. Ecosystems support all life on Earth. The healthier our ecosystems are, the healthier the planet – and its people. The UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration aims to prevent, halt and reverse the degradation of ecosystems on every continent and in every ocean.” TOGETHER WE CAN BE #GENERATIONRESTORATION
TOGETHER WE CAN BE #GENERATIONRESTORATION (Images above – Tom Mcsherry, available on
(Images above – Tom Mcsherry, available on 



