by Ria Olivier | May 10, 2023 | Current Event, Marion Island, News, Overwintering Team, Prince Edward Islands, Research, SANAP, SAPRI, Science, Southern Ocean, Stations, sub-Antarctic, Team member

| TEAM | MAPRU | Affiliation |
| Project Name | Avian scavengers & seabirds |
| Principal Investigator | Dr Maëlle Connan | MAPRU, Nelson Mandela University |
| Co-Investigator | Prof Peter Ryan | Fitzpatrick Institute of African Ornithology, University of Cape Town |
| M79 Field Assistant | Lucy Smyth | MAPRU, Nelson Mandela University |
| M80 Field Assistant | Christopher Jones | MAPRU, Nelson Mandela University |
| M80 Field Assistant | Michelle Risi | MAPRU, Nelson Mandela University and the South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI) |
This team is studying seabirds at Marion Island and has two projects for the period 2021-2023:
1) Avian scavenger project focusing mostly on Black-faced Sheathbill, Kelp Gull and Brown Skua as well as some of their prey.
2) FitzPatrick long-term monitoring of Wandering Albatross, Grey-headed Albatross and Northern Giant Petrel.
More about the avian scavenger project:
This project started in 2021. It is tightly linked to the Mouse-Free Marion project.
Our aim is two fold: 1) we fill identified scientific gaps at the bird level that are crucial for best planning of the mouse eradication and development of appropriate mitigation measures. We are mostly focusing on three species of avian scavengers: Black-faced Sheathbill, Kelp Gull and Brown Skua and some of their prey. 2) we propose to use the three scavengers as indicators of recovery of the terrestrial ecosystem post-eradication by establishing baselines for the scavenger guild and their prey against which the impact of a successful mouse eradication can be measured in years to come.
More about the FitzPatrick long-term monitoring project:
The FitzPatrick long-term monitoring of Wandering and Grey-headed albatrosses and Northern Giant Petrel started in the early 1980s and has continued ever since. This individual-based monitoring of threatened species allows us to study the threats they face at sea (e.g. fisheries) and on land (e.g. mice) in order to act and decrease these threats and improve the conservation status. The species’ long-term monitoring is crucial as it allows us to decipher abnormal years from long-term trends.
More about the fieldwork:
The two projects above involve for example extensive counts of birds, lots of hiking, observations of bird behavior and record keeping of the activity of known individuals year after year.
-

-
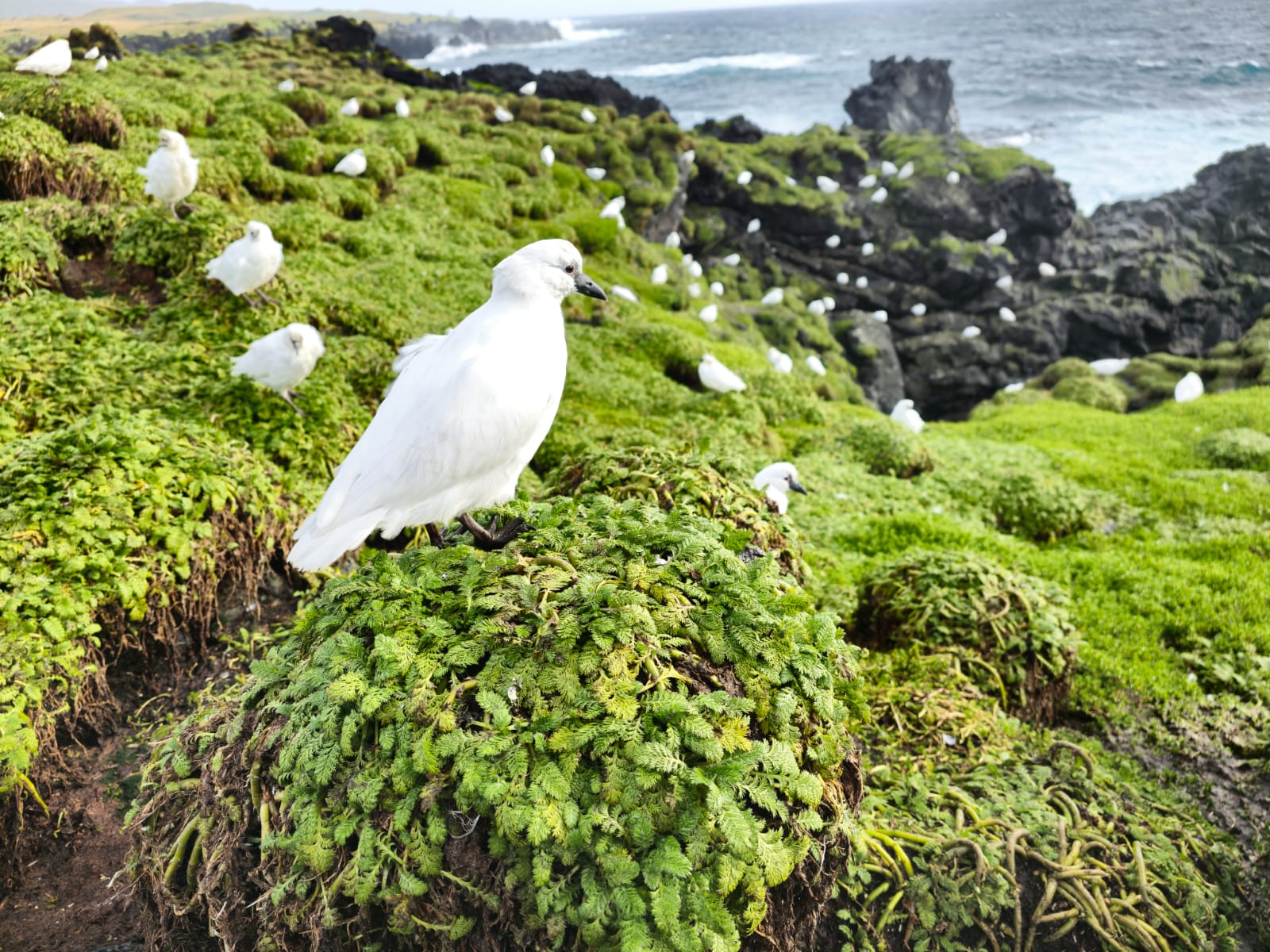
Black-faced Sheathbill count on the West Coast of Marion Island.
-

-
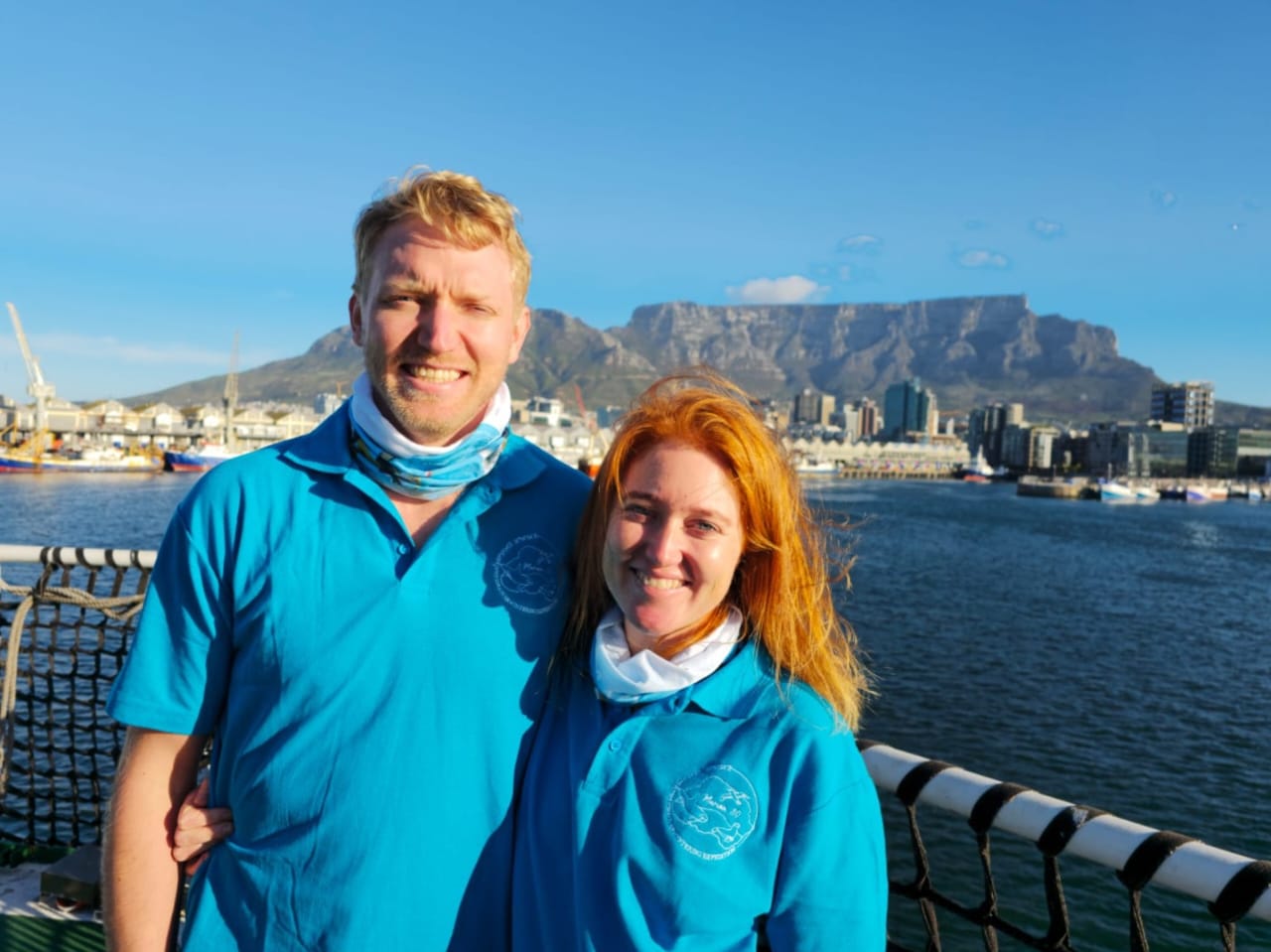
M80 MAPRU Field Assistants: Christopher Jones and Michelle Risi. Image taken on board the S.A. Agulhas II, on the day of departure to Marion Island.
What are your plans for this takeover:
During the takeover, we will be debriefing the year of Lucy Smyth who has worked on the island for our projects since April 2022. We will also train Chris and Michelle for the year ahead in all aspects, from field work to data entry and back-ups.
Follow MAPRU:




Follow PFIAO:




Text by Dr Maëlle Connan.
Images supplied by Christopher Jones.
Featured image: The MAPRU takeover 2023 team. L-R: Dr Maëlle Connan (PI), Lucy Smyth (M79 MAPRU Field Assistant), Michelle Risi (M80 MAPRU Field Assistant) and Christopher Jones (M80 MAPRU Field Assistant). Image taken on the Western side of the island.
Anche Louw, South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI DPS Node), 10 May 2023

by Ria Olivier | May 5, 2023 | Invasion Biology, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, News, Prince Edward Islands, Research, SA Agulhas II, SANAP, Southern Ocean, Stations, sub-Antarctic, Team member

| TEAM | Mouse-Free Marion |
| Project Name | Longitudinal monitoring of terrestrial diversity to assess the effects of the planned mouse eradication on Marion Island, and bait and mouse trials to inform further planning for the Mouse-Free Marion Project |
| Project Manager | Dr Anton Wolfaardt |
| Collaborator | Prof. Michelle Greve |
| M79 Field Assistant | Elsa van Ginkel |
| M80 Field Assistant | Camilla Smyth |
The Mouse-Free Marion Project is a partnership between the Department of Forestry Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE) and BirdLife South Africa, working towards an operation to eradicate invasive mice from Marion Island.
The mice, which were introduced accidentally some 200 years ago, have caused great harm to the ecology of Marion Island. They feed on indigenous invertebrates, damage vegetation, and have more recently started eating seabird chicks. As a result, the mice are considered to be a major pest to the island. If they are not removed, the ecosystem of the island will continue to deteriorate, and they will likely cause most of the seabirds on the island to become locally extinct. These seabirds will be lost to the island forever.
-

-
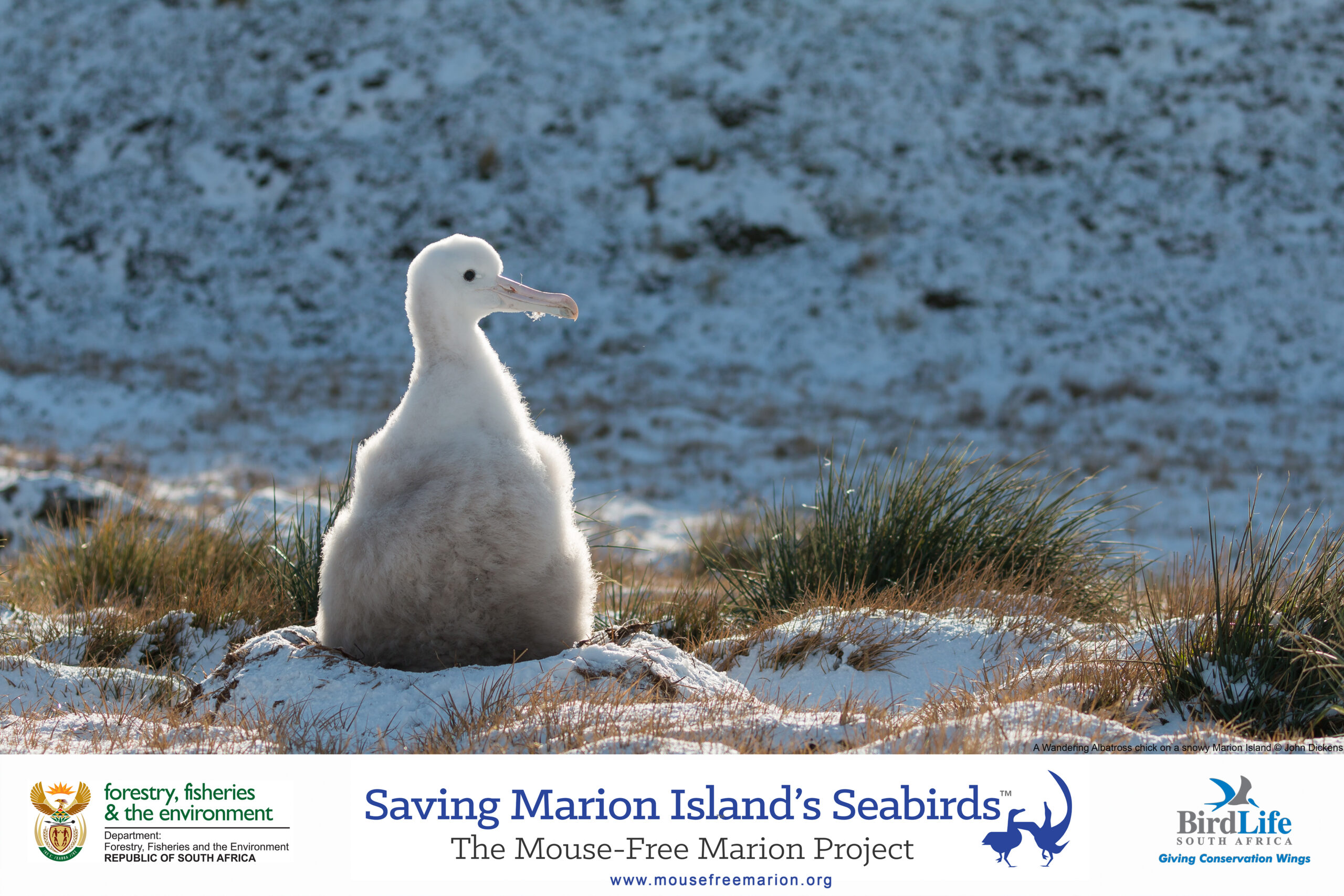
Wandering Albatross chick on nest. Photo Credit: John Dickens, www.mousefreemarion.org
-

-
Northern Giant Petrel. Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie, www.mousefreemarion.org
In order to monitor how the island recovers after the mice have been removed, we are collecting data on aspects of the island that we expect to improve once the mice are gone. These include the vegetation and invertebrates. Colleagues working on other projects are collecting similar data on seabirds.
The reason why it is important to collect this data before the eradication operation is so that we can compare and monitor how the island changes (improves) as a result of the eradication operation – comparing the island’s vegetation and invertebrate features before and after the operation.
More about your plans for this takeover?
The project will make use of data that have already been collected over many years, primarily through the various long-term monitoring projects that have been undertaken at Marion Island over many years. The focus of our work currently is to fill some pre-eradication (baseline) data on vegetation and invertebrates. This particular work was initiated during the 2022/23 period, and will continue in 2023/24. The takeover period will be used to provide training and orientation to the new Marion80 overwintering team member (Camilla Smyth) and for the current Marion79 Mouse-Free Marion overwintering team member (Elsa van Ginkel) to hand over the field-work responsibilities to Camilla.
The work includes standard invertebrate and vegetation survey techniques to establish a baseline that can be used to monitor how these ecological parameters change following the eradication of invasive mice. These surveys will repeat and build on historical surveys that have been undertaken on the island previously.
We will also be undertaking further bait trials and weather monitoring to help inform the planning of the baiting operation.
Latest takeover update from the island (on 26 April 2023)


Check out the Mouse-Free Marion Website!
Follow MFM on social media for the latest updates:


Text and images supplied by Dr Anton Wolfaardt.
Featured image: The MFM takeover 2023 team. L-R: Dr Anton Wolfaardt (MFM Project Manager), Camilla Smyth (M80 MFM Field Assistant) and Elsa van Ginkel (M79 MFM Field Assistant). Photo taken on Marion Island, April 2023.
Anche Louw, South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI DPS Node), 05 May 2023

by Ria Olivier | May 2, 2023 | Current Event, Mammology, Marion Island, News, Research, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean, sub-Antarctic

| TEAM | MIMMP |
| NRF-SANAP Funded Project Name | Marion Island Marine Mammals in Changing Environments: Individual Heterogeneity and Population Processes |
| Principal Investigator | Prof Nico de Bruyn |
| Affiliation | Mammal Research Institute, University of Pretoria |
| Takeover Sealer | Yinhla Shihlomule |
| M79 Sealer | Michael Ross |
| M79 Sealer | Banele Dosi |
| M79 Killer whaler | Monica Leitner |
| M80 Sealer | Zafar Monier |
| M80 Sealer | Dylan Seaton |
| M80 Killer whaler | Tammy Eggeling |
-
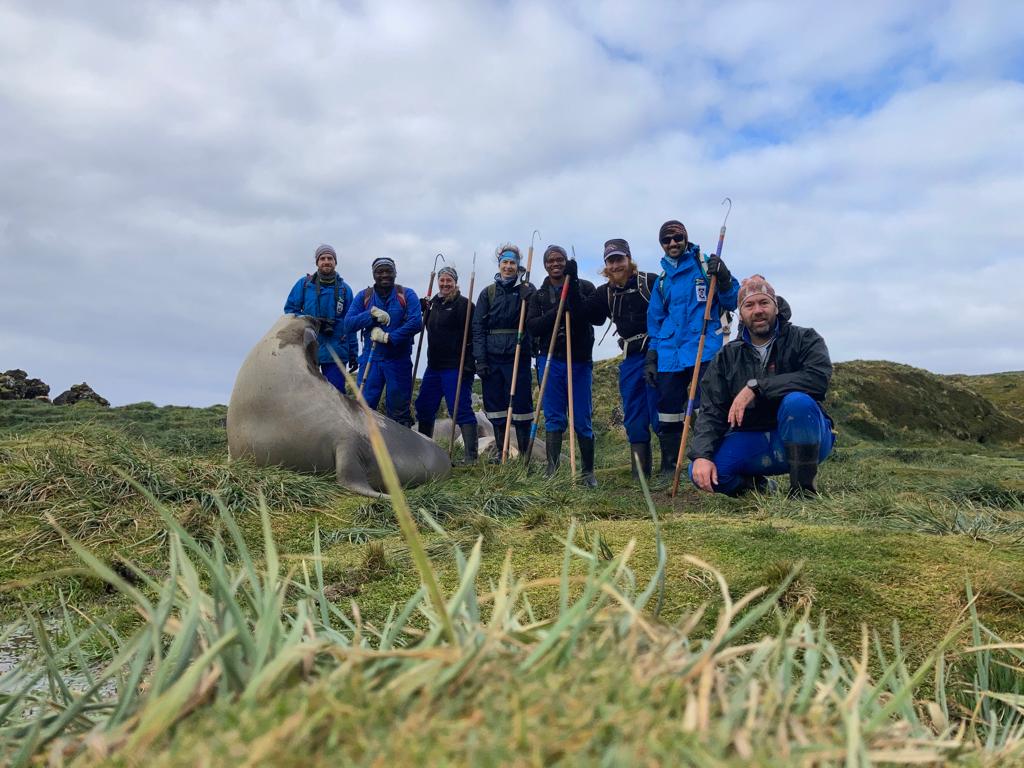

-
MIMMP Sealers and Killer whalers. L-R: a young elephant seal, Dylan, Yinhla, Monica, Tammy, Banele, Mike, Zafar and Nico.
-
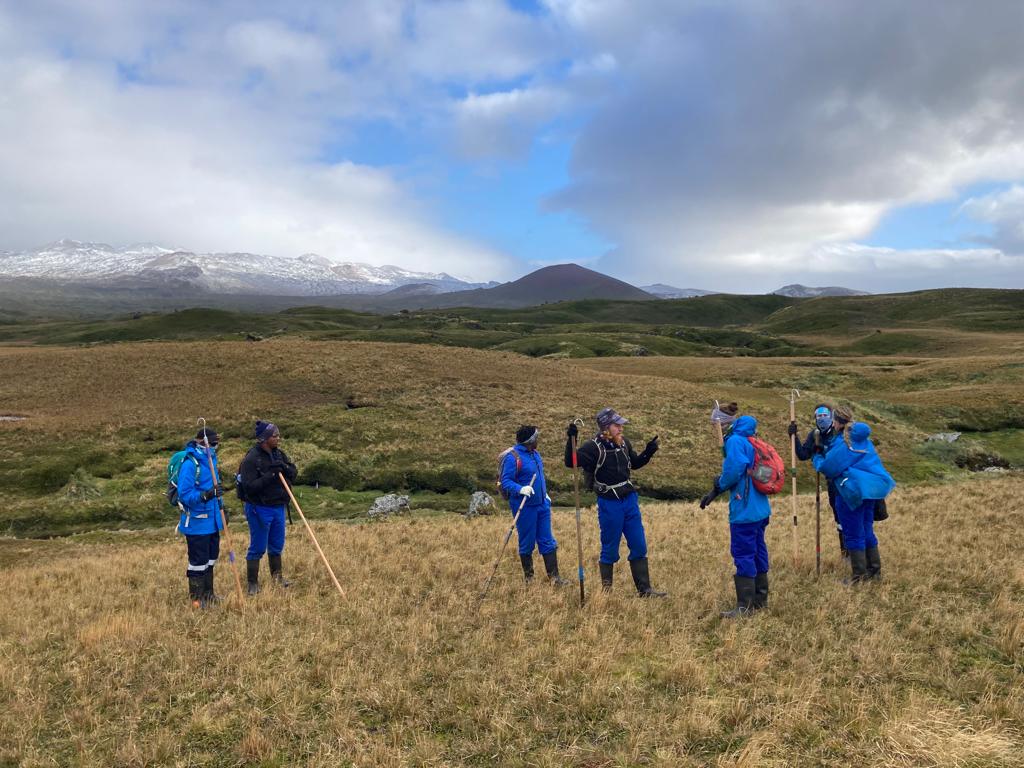

-
First walk out for the full 2023 MIMMP takeover group. An easy introduction into the island, orientation and walking.
What are your plans for this takeover?
Into our 41st uninterrupted year of continuous monitoring! Takeover is mostly dedicated to training the new overwintering personnel, because most of the action (from a seal perspective) on the island take place outside takeover timeframes. Many long-term questions, aimed at understanding the ecology of the various species populations and their interactions with a changing environment, are pursued.
What are the main interest of the MIMMP in the sub-Antarctic region?
We are interested in how seal and killer whale populations change as the environment changes.
In more detail:
MIMMP does long-term ecological monitoring and research of four marine mammal species (Southern elephant seals, Antarctic – and Subantarctic fur seals, and Killer whales) at Marion Island. Focused primarily on population and foraging ecology, interactions between species and with their changing environments.

Check out the MIMMP Website!
Follow MIMMP on social media for the latest updates:



Most recent post on Facebook:

Text and images supplied by Prof Nico de Bruyn.
Featured image: The MIMMP takeover 2023 team. L-R: Dylan Seaton (M80 Sealer), Zafar Monier (M80 Sealer), Prof Nico de Bruyn (PI) and Tammy Eggeling (M80 Killer whaler). Photo taken in Cape Town, on board the S.A Agulhas II, before departure.
Anche Louw, South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI DPS Node), 02 May 2023

by Ria Olivier | Apr 21, 2022 | Current Event, Marion Island, News, Overwintering Team, Prince Edward Islands, Research, SA Agulhas II, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean, Stations, sub-Antarctic, Take-Over Operations

The S.A. Agulhas II departed from East Pier, V&A Waterfront on her annual Marion Island relief voyage, Sunday 17 April 2022. The expected time of arrival at the island is today, 21 April 2022.
The first leg of the voyage, Oceanographic Leg 1, from Cape Town to Marion Island, was dedicated to underway sampling (the vessel did not stop for sampling to take place).
Once at the island, take-over operations will commence immediately (weather permitting) – all land-based scientists, National Department of Public Works (NDPW) personnel, and take-over personnel (DFFE) will disembark. Cargo will be slung with helicopters to the island and fuel will be pumped to the island. Hereafter, the vessel will depart from Marion Island on the 2nd Oceanographic leg (annual Research and Monitoring programme around the Prince Edward Islands). The 3rd Oceanographic leg will commence after take-over, on the way back to Cape Town.
What is planned for the 2022 take-over on Marion Island (land-based)
- base and hut maintenance (NDPW)
- base and hut restock
- take-over function
- 79th Marion Island overwintering team (meet the team in next article) to take over from 78th Marion Island overwintering team (M78 – click here).
- take-over projects – scientific fieldwork (see table below)
What is planned for the take-over onboard the S.A. Agulhas II (ship-based)
DFFE: Ocean & Coasts Research
DFFE Ship-based Southern Ocean and Islands Research Programme |
| Ocean Physics: Group Leader | Mr Gavin Tutt |
| Ocean Chemistry: Group Leader | Dr Thato Mtshali |
| Ocean Biological: Group Leader | Mr Henry Kakora |
DFFE:Ocean & Coasts, University of Cape Town, Bayworld Centre for Research & Education
SAMOC-SA |
| Group Leader | Mr. Grant van der Heever |
University of Pretoria
Enhanced insights regarding the ecology, evolution, and function of marine microbiomes |
| Group Leader | Mr Choaro Dithugoe |
Land-based DFFE and other take-over personnel
Department of Forestry Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE)
Directorate: Southern Oceans & Antarctic Support
Management, logistics and support for this voyage |
| Departmental Co-ordinator (DCO) | Mr Errol Julies |
| Assistant DCO | Mr Mfundo Tima |
| Admin Officer | Ms Pozisa Matshoba |
| General/Waste Technician | Mr Sabata Setona |
| General/Waste Technician | Mr Mazizi Salmani |
DFFE
Directorate: Oceans, Coasts & Biosecurity Compliance |
| Environmental Control Officer | Mr Thomas Mufanadzo |
DFFE
Directorate: Earth Systems Strategies
Prince Edward Islands Management Authority (Oversight Management Functions) |
| Group Leader | Ms Ntombovuyo Madlokazi |
| Chief Scientists |
| Land-based | Prof Werner Nel |
| Ship-based | Mr Marcel van den Berg |
National Department of Public Works (NDPW)
Maintenance Support |
| Group Leader | Mr Takalani Mudau |
Featured Image: S.A. Agulhas II at Marion Island, May 2014 (Credit: Anche Louw).
Anche Louw, Antarctic Legacy of South Africa, 21 April 2022

by Ria Olivier | Jul 5, 2021 | Biosecurity, Environment, Invasion Biology, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Research, Science


 Marion Island (29 000 hectares) and Prince Edward (4500 hectares), collectively known as the Prince Edward Islands (PEIs) were annexed by South Africa in December 1947 and January 1948, respectively. Since then, South Africa has maintained a research and weather station on Marion Island, Prince Edward remains uninhabited. The PEIs were declared a Special Nature Reserve in 1995, a Ramsar Wetland Site of International Importance in 2007 and the surrounding waters a Marine Protected Area in 2009. The islands, governed by a suite of national environmental legislation under the Prince Edward Islands Management Plan (which includes a plan for the control and eradication of invasive alien species), are managed by the Oceans and Coasts Branch of the Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE) as the designated Management Authority under the National Environmental Management Protected Areas Act 57 of 2003.
Marion Island (29 000 hectares) and Prince Edward (4500 hectares), collectively known as the Prince Edward Islands (PEIs) were annexed by South Africa in December 1947 and January 1948, respectively. Since then, South Africa has maintained a research and weather station on Marion Island, Prince Edward remains uninhabited. The PEIs were declared a Special Nature Reserve in 1995, a Ramsar Wetland Site of International Importance in 2007 and the surrounding waters a Marine Protected Area in 2009. The islands, governed by a suite of national environmental legislation under the Prince Edward Islands Management Plan (which includes a plan for the control and eradication of invasive alien species), are managed by the Oceans and Coasts Branch of the Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE) as the designated Management Authority under the National Environmental Management Protected Areas Act 57 of 2003.
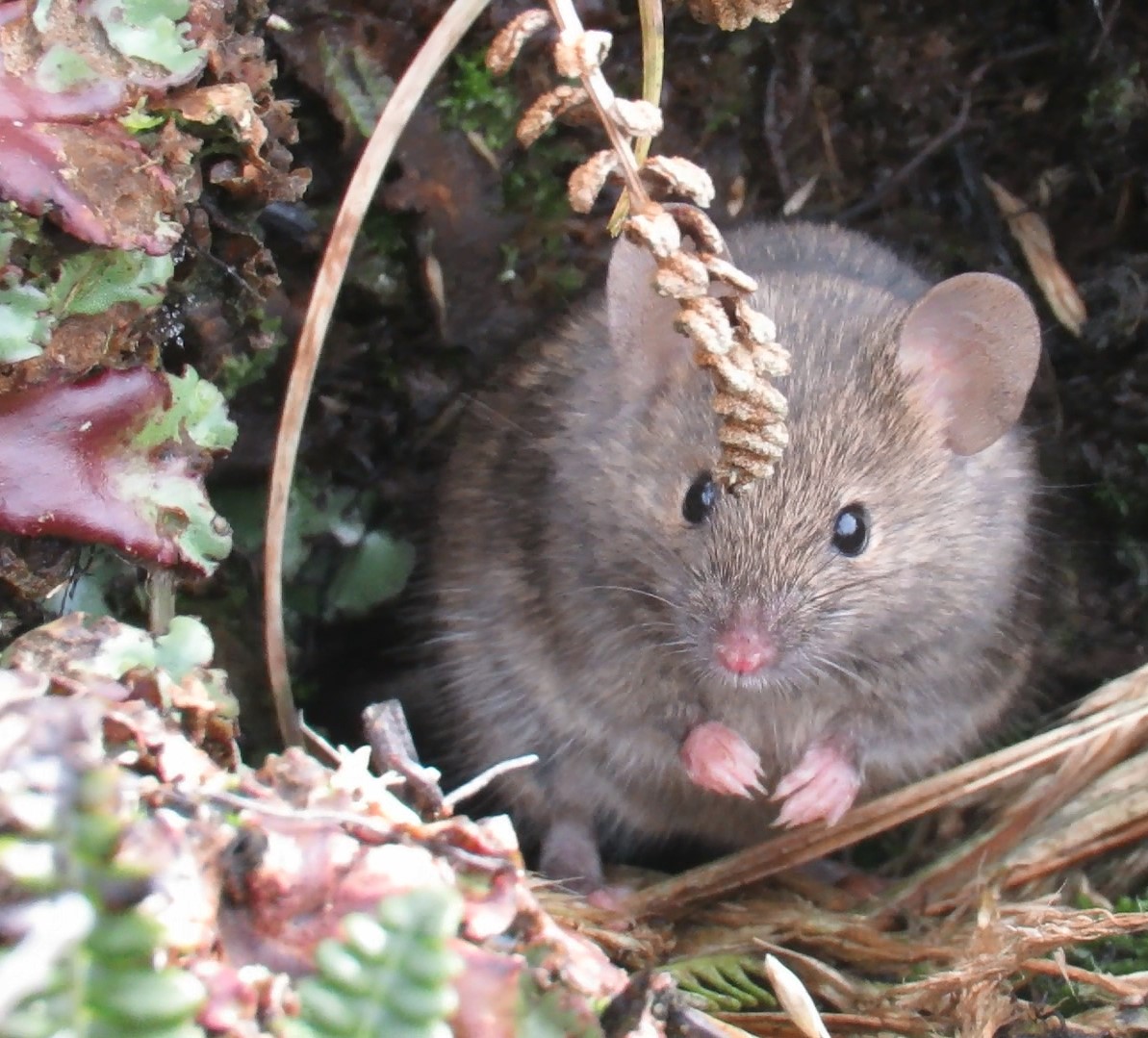
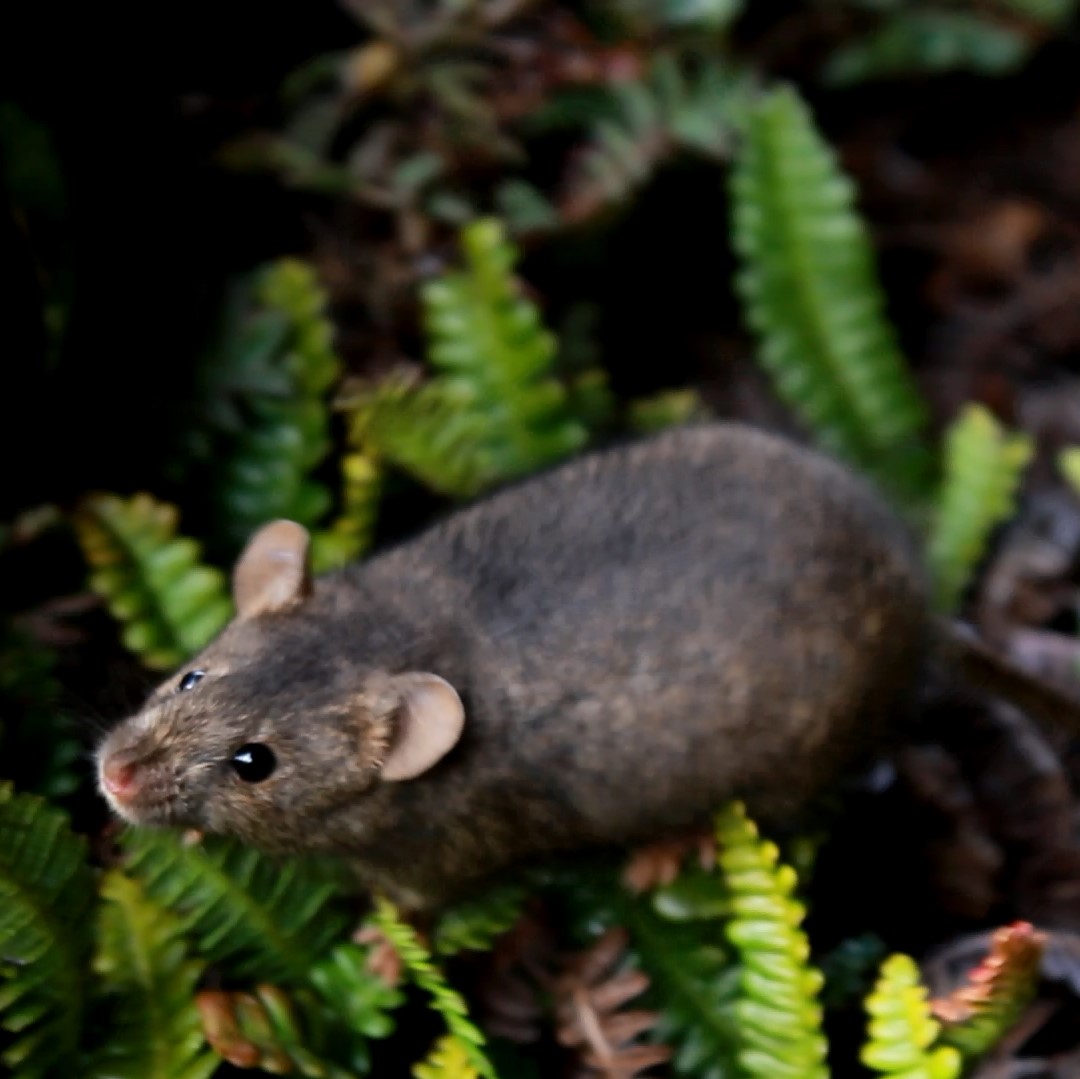
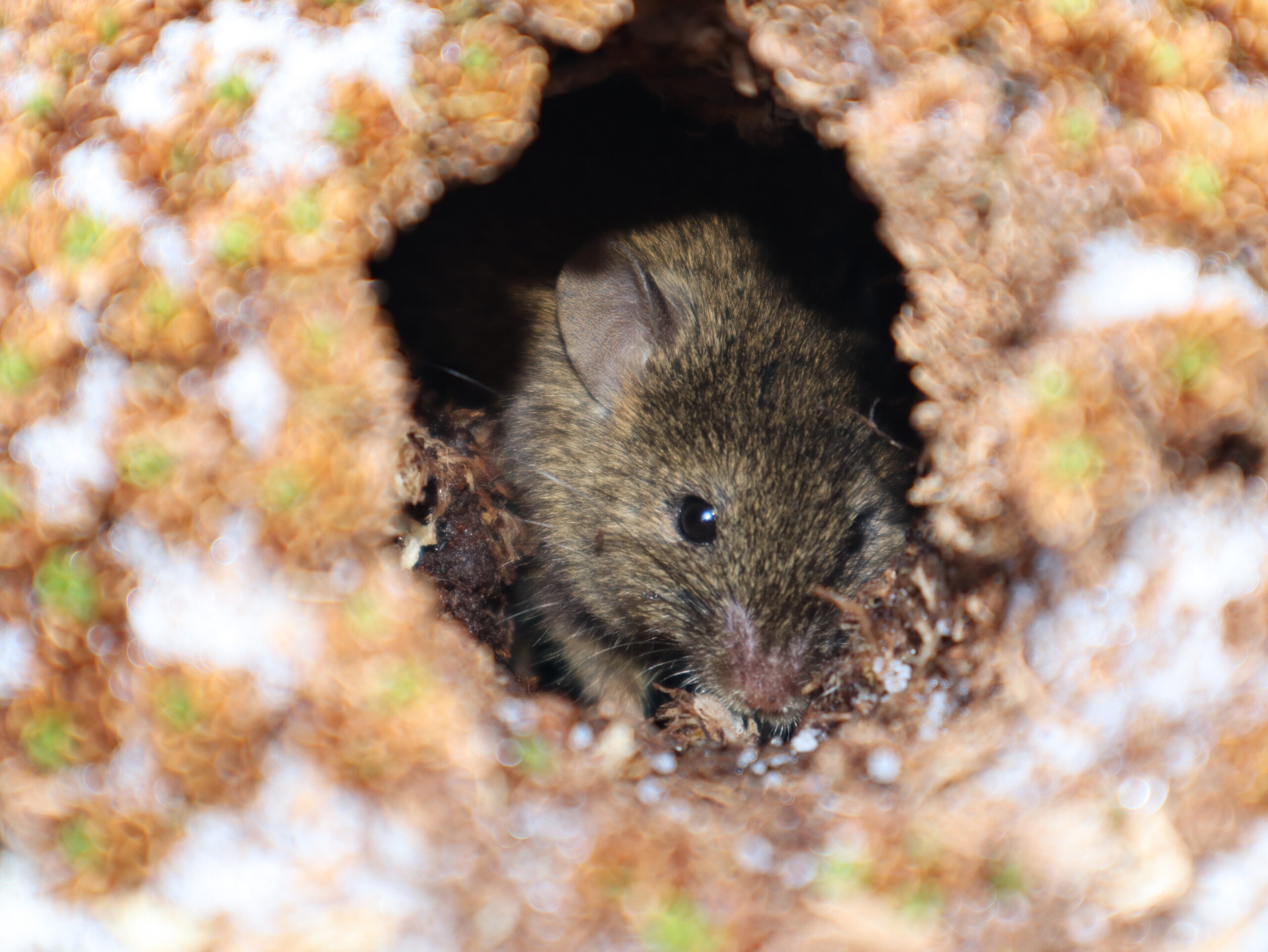

 The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.
The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.
 With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)
With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)
Marion Island supports some 25% of the world’s breeding population of Wandering Diomedea exulans, 12% of Sooty Phoebetria fusca and 7% of Grey-headed Thalassarche chrysostoma Albatrosses and smaller percentages of Light-mantled Albatrosses P. palpebrata and Grey Petrels Procellaria cinerea. It is clear something needs to be done or the severe impact of the mice could result in critical impacts on global populations and in the extirpation of up to 18 of the 27 bird species found on Marion within the next 30 to 100 years. (below l-r: Wandering Albatross, Sooty Albatross and chick, Grey-headed Albatross and chick. (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie)



 In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a Feasibility Study and Risk Assessment, undertaken in 2016 by John Parkes on behalf of BirdLife South Africa (BLSA), indicated that eradication was indeed possible. Also funded by BLSA, Draft Project and Operational Plans to eradicate mice on Marion Island were subsequently developed in 2018 by New Zealand eradication expert, Keith Springer, following an island visit. DFFE has been working closely with the UK’s Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) over the last few years in support of the Gough Island Restoration Programme (GIRP) which aims to eradicate House Mice on Gough during June to September 2021. For more information and the latest updates on the GIRP, please visit: https://www.goughisland.com
In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a Feasibility Study and Risk Assessment, undertaken in 2016 by John Parkes on behalf of BirdLife South Africa (BLSA), indicated that eradication was indeed possible. Also funded by BLSA, Draft Project and Operational Plans to eradicate mice on Marion Island were subsequently developed in 2018 by New Zealand eradication expert, Keith Springer, following an island visit. DFFE has been working closely with the UK’s Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) over the last few years in support of the Gough Island Restoration Programme (GIRP) which aims to eradicate House Mice on Gough during June to September 2021. For more information and the latest updates on the GIRP, please visit: https://www.goughisland.com
On 12 May 2020, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the Mouse-Free Marion (MFM) Project was signed between DFFE and BLSA. Subsequently, a MFM Management Committee was established to initiate the development of the project and the two MoU partners are now working closely, together with various experts and institutions (including those involved with successful operations on other islands), on the detailed planning on all operational aspects required for the execution of this complex and costly project.


The MFM Project will make use of internationally agreed best-practice approaches to eradicate mice from the island. The Feasibility Study and draft Project and Operational Plans highlight that the only methodology offering any chance of success on an island of the size and topography of Marion Island is aerial spreading of bait containing a rodenticide with a proven capacity to eradicate mice.  The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the base and other infrastructure on the island. If a single pregnant female is not targeted, it could result in the failure of the entire operation, but if it works, Marion Island will be by far the largest island in the world from which House Mice have successfully been eradicated.
The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the base and other infrastructure on the island. If a single pregnant female is not targeted, it could result in the failure of the entire operation, but if it works, Marion Island will be by far the largest island in the world from which House Mice have successfully been eradicated.
Time window trade-offs have been assessed and it has been determined that winter (April/May – August/September) is the optimal period in which to implement an eradication operation. This is the non-breeding period for mice at Marion, when their population size is low and natural food resources are minimal, rendering bait more attractive. A winter-baiting operation also reduces the risks to non-target seabird species on the island, as many are not resident on the island during the winter months.
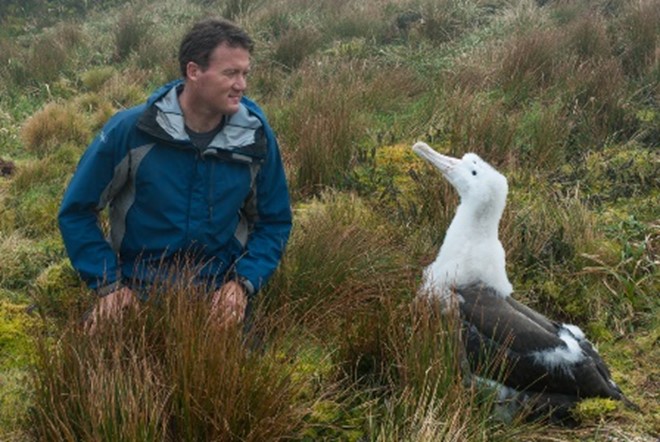
Currently, the eradication exercise is planned for the austral winter of 2023 and, to review and update the Project and Operational Plans, a Project Manager (Dr Anton Wolfaardt – photo left) and an Operations Manager (Mr Keith Springer – photo right) have been appointed.


 A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘Sponsor a Hectare’ (which is currently standing at just over R2 million), please visit http://www.mousefreemarion.org.za
A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘Sponsor a Hectare’ (which is currently standing at just over R2 million), please visit http://www.mousefreemarion.org.za
Text compiled by Carol Jacobs - Directorate: Biosecurity (DFFE)
Images from Marion Mouse Free Project, Stefan Schoombie,
FitzPatrick Institute and Antarctic Legacy of South Africa digital archive.
Cover Image: Otto Whitehead
,
























 Marion Island (29 000 hectares) and Prince Edward (4500 hectares), collectively known as the Prince Edward Islands (PEIs) were
Marion Island (29 000 hectares) and Prince Edward (4500 hectares), collectively known as the Prince Edward Islands (PEIs) were 

 The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.
The House Mouse Mus musculus (Photo Credit: Stefan Schoombie), inadvertently introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 1800s, successfully established on the island. With the human occupation of the island in 1948, four cats were brought to the island to control the mice in and around the station. However, these cats bred on the island, with their offspring becoming feral, and by the 1970s the population had increased to about 2000 individuals that were killing some 450 000 birds per year, mostly chicks of burrow-nesting species.  With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)
With South Africa’s successful eradication of the cats in 1991 (confirmed in 1992), until recently the largest island upon which this has been achieved, the mice continued to thrive and over the years have had devastating effects on Marion’s fragile ecosystem by negatively affecting invertebrate densities, impacting on the vegetation by consuming seed loads and preying upon the chicks of burrowing petrels (since the 1980s) and surface-breeding albatrosses (since 2003), with ‘scalpings’ occurring from 2009 and attacks on adult birds recorded more recently in 2019. (Image Credit: FitzPatrick Institute)


 In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a
In what would later become a partnership with DFFE, a 

 The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the
The systematic aerial sowing of bait will be conducted by GPS-guided helicopters with underslung bait buckets to ensure every single mouse territory is covered. The aerial baiting will be complemented by hand-baiting approaches in and around the 

 A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘
A project of this nature requires substantial funding. To date, funds provided and committed are comprised largely of donations, government funding and crowd sourcing to save Marion Island’s seabirds. For more information and the latest updates on the MFM Project, as well as to ‘