by Ria Olivier | Feb 22, 2024 | Biosecurity, Ecology, Invasion Biology, Marion Island, Research, SANAP, SANAP Student, Uncategorised

 Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren (left) chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery with the first plenary talk of the symposium by Peter Convey(right) of the British Antarctic Survey ” Terrestrial biological invasions and their potential impacts in the maritime Antarctic”. (Abstract) Peter Convey discussed that there are around 15 species of non-native plants and invertebrates currently known to be established in the maritime Antarctic . He further emphasize that effective biosecurity measures are required to ensure that further human-assisted transfer both on Signy Island and beyond is avoided. Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery.
Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren (left) chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery with the first plenary talk of the symposium by Peter Convey(right) of the British Antarctic Survey ” Terrestrial biological invasions and their potential impacts in the maritime Antarctic”. (Abstract) Peter Convey discussed that there are around 15 species of non-native plants and invertebrates currently known to be established in the maritime Antarctic . He further emphasize that effective biosecurity measures are required to ensure that further human-assisted transfer both on Signy Island and beyond is avoided. Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery.
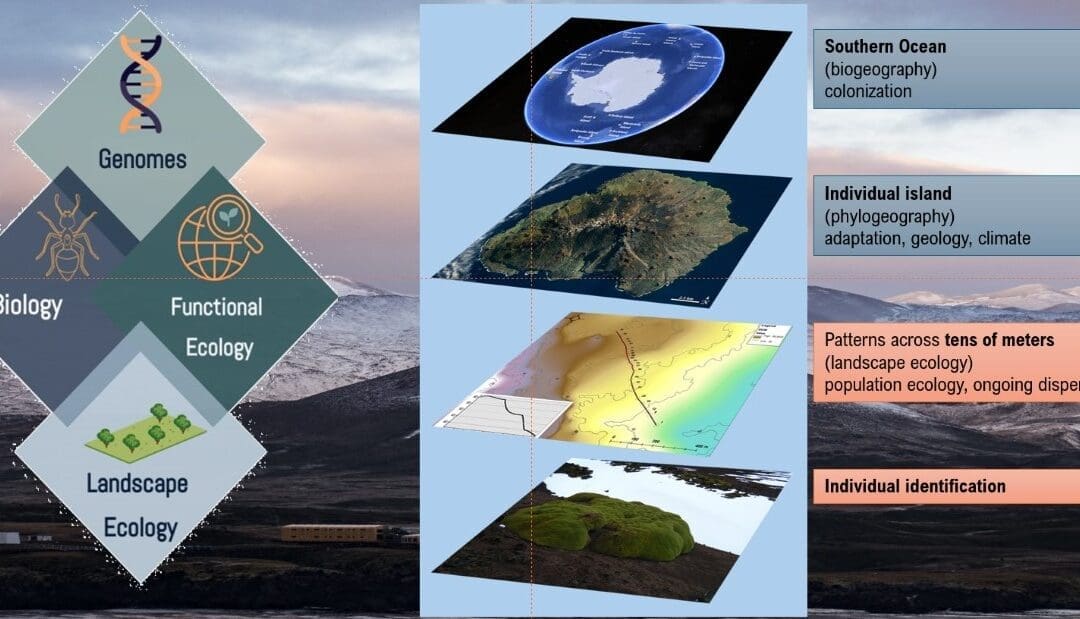
 Bettine gave an overview of research that included research done by Daniela and Shilpha as they could not attend as they were on Marion Island. Foregrounding geodiversity in landscape ecology studies: insights from the sub-Antarctic – Daniela Monsanto (Abstract) Detecting signals of adaptive selection of an invasive springtail on sub-Antarctic Marion Island – Shilpha Parbhu (Abstract)
Bettine gave an overview of research that included research done by Daniela and Shilpha as they could not attend as they were on Marion Island. Foregrounding geodiversity in landscape ecology studies: insights from the sub-Antarctic – Daniela Monsanto (Abstract) Detecting signals of adaptive selection of an invasive springtail on sub-Antarctic Marion Island – Shilpha Parbhu (Abstract)
 Daniela Monsanto, Shilpa Parbhu, Sandra Durand, Arsalan Emami-Khoyi, Peter Teske, David Hedding
Daniela Monsanto, Shilpa Parbhu, Sandra Durand, Arsalan Emami-Khoyi, Peter Teske, David Hedding
 Morgan Raath-Kruger(left) and student of Peter le Roux at University of Pretoria gave an oral presentation and an introduction to her poster.
Morgan Raath-Kruger(left) and student of Peter le Roux at University of Pretoria gave an oral presentation and an introduction to her poster.
- Long-term spatially-replicated data show no physical cost to a benefactor species in a facilitative plant–plant interaction. (Abstract)
- Do anisotropic processes influence fine-scale spatial genetic structure of a keystone sub-Antarctic plant species? (Abstract)
 Another abstract submitted but Carol Jacobs(right) could not present is on the biosecurity within the South African National Antarctic Programme. (Abstract)https://alp.lib.sun.ac.za/handle/123456789/29301
Another abstract submitted but Carol Jacobs(right) could not present is on the biosecurity within the South African National Antarctic Programme. (Abstract)https://alp.lib.sun.ac.za/handle/123456789/29301

by Ria Olivier | Jan 29, 2024 | Ecology, Invasion Biology, Jobs, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Overwintering Team, SANAP, sub-Antarctic, Team member
Vacancy for Mouse-Free Marion (MFM) Project Research Assistant on Marion Island (March 2024 – May 2025)

BirdLife South Africa, via the Mouse-Free Marion (MFM) Non-Profit Company (NPC), is offering an opportunity to a suitably qualified candidate to spend a year on Marion Island to continue monitoring studies designed to support the ongoing planning for the mouse-eradication operation. The position will include collecting field data on mice, continuing the monitoring of weather parameters, undertaking further field trials relating to the bait and, in collaboration with the University of Pretoria, contributing to the collection of baseline data on invertebrates and plants.
To read more about the Mouse Free Marion project – Click here
CLOSING DATE 12 FEBRUARY 2024
Read more about Marion Island and Overwintering Teams on the SANAP website
Key Responsibilities on Marion Island and Basic Academic Requirements, Experience, and Skills are is listed in the advertisement.
At least a B.Sc. (Hons) degree in conservation biology, ecology, or a related field.
Experience of field work in rugged terrain is required.
Please e-mail your application to Dr Isabel Human, at isabel.human@birdlife.org.za see relevant documents to be included in advertisement
South African applicants will receive priority. Please note that appointments will be contingent on availability of ship berths and funding.
For queries contact Dr. Sue Tonin, the Mouse-Free Marion Assistant Project Manager, at sue.tonin@birdlife.org.za

by Ria Olivier | Jan 25, 2024 | Ecology, Invasion Biology, Jobs, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Overwintering Team, SANAP, sub-Antarctic, Team member
 Vacancy for field researcher on Marion Island (March 2024 – May 2025) –
Vacancy for field researcher on Marion Island (March 2024 – May 2025) –
Mouse impacts on invertebrates and plants
 The Department of Plant and Soil Sciences at the University of Pretoria is offering one suitably qualified candidate an opportunity to spend a year on Marion Island to measure various aspects of the impact of the house mouse on the diversity and function of the terrestrial ecosystems of Marion Island. This work will entail collecting baseline data, mostly on invertebrates and plants.
The Department of Plant and Soil Sciences at the University of Pretoria is offering one suitably qualified candidate an opportunity to spend a year on Marion Island to measure various aspects of the impact of the house mouse on the diversity and function of the terrestrial ecosystems of Marion Island. This work will entail collecting baseline data, mostly on invertebrates and plants.
CLOSING DATE 4 FEBRUARY 2024
Read more about Marion Island and Overwintering Teams on the SANAP website
REQUIREMENTS (full list available in advertisement
Minimum BSc (Hons) degree in an ecological field.
Experience of field work in rugged terrain is required.
Excellent organisational skills, attention to detail, meticulous observation, note-taking
and record-keeping abilities.
Experience of invertebrate and/or plant surveys.
Computer literacy with experience in data management, statistical analysis (at least
one undergraduate statistics course) and report writing are required.
Applicants should submit their applications here.
South African applicants will receive priority. Please note that appointments will be contingent on availability of ship berths and funding.
For queries contact Prof Greve (michelle.greve@up.ac.za) via email.

by Ria Olivier | Oct 12, 2023 | Environment, Gough Island, Invasion Biology, Mice Eradication, News, Overwintering Team, Research, Science, Take-Over Operations
The Gough Island Restoration Programme

Situated in the South Atlantic Ocean, positioned equidistantly between South Africa and South America, lies a highly significant breeding ground for seabirds known as Gough Island. This remote island serves as the breeding habitat for 24 distinct avian species, many of which are found nowhere else on the planet. Regrettably, the avian inhabitants now share their home with an invasive species, specifically the house mouse. These non-native mice, introduced to the island by human activity, are causing severe harm to the island’s native wildlife, including plants and animals that have thrived there for millennia. The mice’s voracious appetite leads to the consumption of over two million seabird eggs and chicks annually, driving certain species perilously close to extinction.
In an effort to safeguard the birds, the Gough Island Restoration Programme was launched with the aim of eradicating the mice. In 2021, the Gough Island Restoration Programme attempted to eradicate mice from the island in one of the most challenging and logistically complex island eradications ever ventured.
Although the endeavor did not achieve complete success, it significantly reduced the mouse population, providing a respite for the birds. During this period, the avian inhabitants managed to successfully raise numerous chicks.
Scientists continue to monitor the birds and gather valuable information that will hopefully aid in future endeavors to eliminate the mice entirely. Part of this takeover and the overwintering field team’s work programme will relate to follow-up activities to further underpin efforts to restore Gough Island.
| Team | The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) |
| Project Name | The Gough Island Restoration Programme |
| Principal Investigator | Dr Antje Steinfurth |
Field Team Leader
(Gough68 & Gough69) | Dr Lucy Dorman |
| Field Officer (Gough68) | Ms Rebekah Goodwill |
| Field Officer (Gough69) | Ms Hannah Greetham |
More about the work on the island for this takeover:
“During takeover our team is carrying out a census of Tristan Albatrosses and Southern Giant Petrels across the whole island, the so-called round island survey. At this time of year, the Southern Giant Petrels are starting to breed while the Tristan Albatross chicks are about to fledge. The number of fledged Albatross chicks will then be compared to numbers of breeding pairs that were counted at the beginning of the year and so breeding success for this Critically Endangered bird can be calculated (more than 99% of the global population breed exclusively on Gough Island). The round island survey also provides the team with the opportunity to monitor the abundance and distribution of the two landbird species, the Gough Bunting and the Gough moorhen.
This takeover the team will also be taking some soil samples from the upland parts of the island. This is to help monitor the ecosystem in the wake of the mouse eradication attempt”.

The RSPB Gough Island Restoration Programme takeover team (L-R): Hannah Greetham, Antje Steinfurth, Lucy Dorman and Rebekah Goodwill.
The RSPB overwintering team members’ work:
They will focus on Gough’s bird life, monitoring the breeding success of species, providing estimates of their populations and survival and documenting the impacts of House Mice.
For more information visit about The Gough Island Restoration Programme, click on the link below.
The Gough Island Restoration Programme This project is funded by: The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB).
This project is funded by: The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB).
Project information and images supplied by Dr Antje Steinfurth.
Anche Louw, South African Polar Research Infrastructure, 12 October 2023.

by Rabia Mathakutha | Jun 19, 2023 | Antarctica, Current Event, Environment, Important Dates, International Days, Invasion Biology, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Research, SANAP, SAPolarRI, SAPRI, Southern Ocean, sub-Antarctic, Uncategorised
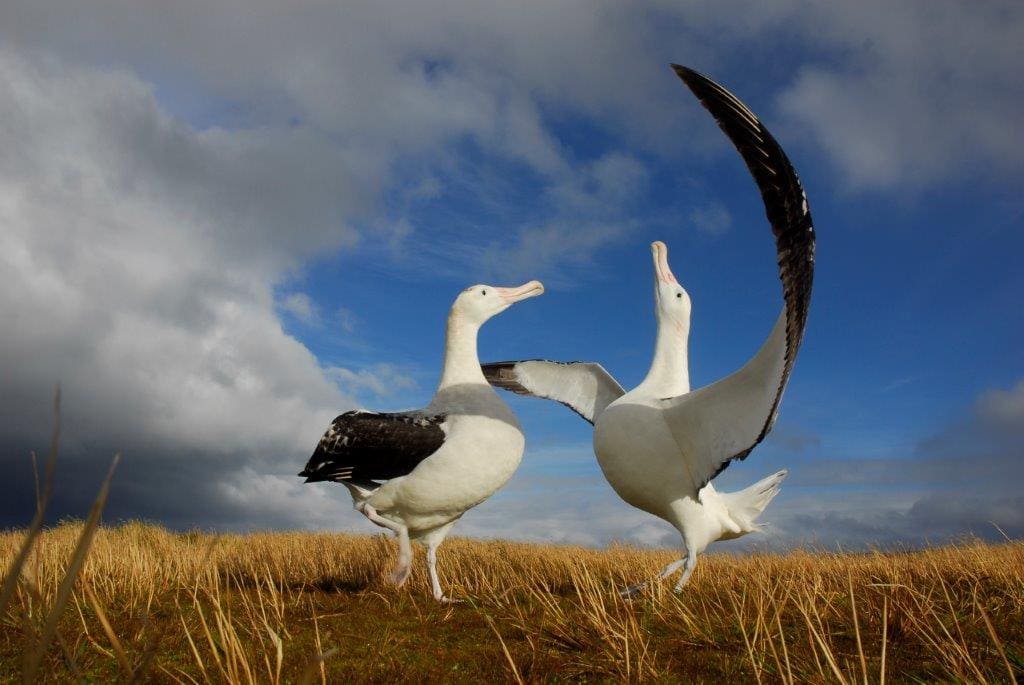
On 19th of June, the world comes together to celebrate World Albatross Day, an annual event dedicated to raising awareness about these magnificent seabirds and the conservation challenges they face. World Albatross Day serves as a crucial platform to educate and inspire action to protect these iconic ocean wanderers. With their graceful flight and important ecological role, albatrosses deserve our attention and concerted efforts for their survival.
South Africa is a long-standing Party to the International Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP). The agreement was brought into existence on 1 February 2004. The day also falls on the date of the signing of the Agreement 22 years ago. ACAP has chosen the theme “Plastic Pollution” to mark the fourth World Albatross Day, to be celebrated on 19 June 2023. This follows the inaugural theme “Eradicating Island Pests” in 2020, “Ensuring Albatross-friendly Fisheries” in 2021, and “Climate Change” last year in 2022.
Albatrosses close to home
Multiple species of albatross are found across the Southern Ocean. This includes Antarctic, sub-Antarctic and subtropical waters. These albatrosses breed on sub-Antarctic and Antarctic islands including South Africa’s sub-Antarctic Marion Island. Marion Island holds significant breeding populations of four albatross species – the Wandering Diomedea exulans, Grey-headed, Light-mantled Phoebetria palpebrata and Sooty Phoebetria fusca. In addition to this, two other species of albatrosses have been seen ashore on Marion Island – Black-browed and Indian Yellow-nosed Thalassarche carteri. To read more about the “other” two species of albatrosses recorded from Marion Island as uncovered by one of our researchers Kim Stevens, click here.
The Challenges Facing Albatrosses
Albatrosses face a range of challenges that threaten their survival. One of the most pressing issues is longline fishing, where albatrosses can become accidentally caught on fishing hooks, leading to injury or death. Pollution, habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species on breeding islands also pose significant risks to their populations. World Albatross Day sheds light on these challenges and promotes measures to mitigate their impact. The pressing threats to Albatrosses in the Southern Ocean include invasive species on breeding islands, most notably, the house mice on Marion Island. Introduced to Marion Island by sealers in the early 19th century, the house mice have been inflicting devastating impacts on the ecology of the island, including killing its native seabirds.
Conservation Efforts and Awareness
The Mouse-Free Marion Project is a registered non-profit company in South Africa, established to eradicate the invasive albatross-killing mice on Marion Island. The project was initiated by BirdLife South Africa and the South African Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE). Upon successful completion, the project will restore the critical breeding habitat of over two million seabirds, many globally threatened, and improve the island’s resilience to a warming climate. For more information or to support the project please visit mousefreemarion.org.
May 2023: Barbara Creecy, Minister of Forestry, Fisheries, Forestry and the Environment, confirms government support for the Mouse-Free Marion Project in her budget speech.
What can you do?
In keeping with this year’s theme for World Albatross Day “Plastic Pollution”, as an individual you can participate by reducing plastic pollution, organising or joining local beach cleanups, where you can help remove litter and prevent it from reaching the oceans, including minimising the use of single-use plastics. Education plays a vital role in driving positive change for albatross conservation. Increase your understanding of albatross biology, their unique adaptations, the threats they face, and the ecological importance they hold in marine ecosystems by reading some of these selected publications here. By raising awareness and fostering partnerships, we can work collectively to safeguard albatross populations and their habitats.
Let us unite in our efforts to protect these majestic ocean wanderers and ensure a future where albatrosses continue to grace our oceans for generations to come.
YOU CAN HELP SAVE MARION ISLAND’S SEABIRDS
Images: The Mouse-Free Marion Project (text added to MFM poster) and Antarctic Legacy of South Africa (ALSA)
Rabia Mathakutha, South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI DPS Node), 19 June 2023

by Ria Olivier | May 5, 2023 | Invasion Biology, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, News, Prince Edward Islands, Research, SA Agulhas II, SANAP, Southern Ocean, Stations, sub-Antarctic, Team member

| TEAM | Mouse-Free Marion |
| Project Name | Longitudinal monitoring of terrestrial diversity to assess the effects of the planned mouse eradication on Marion Island, and bait and mouse trials to inform further planning for the Mouse-Free Marion Project |
| Project Manager | Dr Anton Wolfaardt |
| Collaborator | Prof. Michelle Greve |
| M79 Field Assistant | Elsa van Ginkel |
| M80 Field Assistant | Camilla Smyth |
The Mouse-Free Marion Project is a partnership between the Department of Forestry Fisheries and the Environment (DFFE) and BirdLife South Africa, working towards an operation to eradicate invasive mice from Marion Island.
The mice, which were introduced accidentally some 200 years ago, have caused great harm to the ecology of Marion Island. They feed on indigenous invertebrates, damage vegetation, and have more recently started eating seabird chicks. As a result, the mice are considered to be a major pest to the island. If they are not removed, the ecosystem of the island will continue to deteriorate, and they will likely cause most of the seabirds on the island to become locally extinct. These seabirds will be lost to the island forever.
In order to monitor how the island recovers after the mice have been removed, we are collecting data on aspects of the island that we expect to improve once the mice are gone. These include the vegetation and invertebrates. Colleagues working on other projects are collecting similar data on seabirds.
The reason why it is important to collect this data before the eradication operation is so that we can compare and monitor how the island changes (improves) as a result of the eradication operation – comparing the island’s vegetation and invertebrate features before and after the operation.
More about your plans for this takeover?
The project will make use of data that have already been collected over many years, primarily through the various long-term monitoring projects that have been undertaken at Marion Island over many years. The focus of our work currently is to fill some pre-eradication (baseline) data on vegetation and invertebrates. This particular work was initiated during the 2022/23 period, and will continue in 2023/24. The takeover period will be used to provide training and orientation to the new Marion80 overwintering team member (Camilla Smyth) and for the current Marion79 Mouse-Free Marion overwintering team member (Elsa van Ginkel) to hand over the field-work responsibilities to Camilla.
The work includes standard invertebrate and vegetation survey techniques to establish a baseline that can be used to monitor how these ecological parameters change following the eradication of invasive mice. These surveys will repeat and build on historical surveys that have been undertaken on the island previously.
We will also be undertaking further bait trials and weather monitoring to help inform the planning of the baiting operation.
Latest takeover update from the island (on 26 April 2023)


Check out the Mouse-Free Marion Website!
Follow MFM on social media for the latest updates:


Text and images supplied by Dr Anton Wolfaardt.
Featured image: The MFM takeover 2023 team. L-R: Dr Anton Wolfaardt (MFM Project Manager), Camilla Smyth (M80 MFM Field Assistant) and Elsa van Ginkel (M79 MFM Field Assistant). Photo taken on Marion Island, April 2023.
Anche Louw, South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI DPS Node), 05 May 2023

 Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren (left) chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery with the first plenary talk of the symposium by Peter Convey(right) of the British Antarctic Survey ” Terrestrial biological invasions and their potential impacts in the maritime Antarctic”. (Abstract) Peter Convey discussed that there are around 15 species of non-native plants and invertebrates currently known to be established in the maritime Antarctic . He further emphasize that effective biosecurity measures are required to ensure that further human-assisted transfer both on Signy Island and beyond is avoided. Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery.
Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren (left) chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery with the first plenary talk of the symposium by Peter Convey(right) of the British Antarctic Survey ” Terrestrial biological invasions and their potential impacts in the maritime Antarctic”. (Abstract) Peter Convey discussed that there are around 15 species of non-native plants and invertebrates currently known to be established in the maritime Antarctic . He further emphasize that effective biosecurity measures are required to ensure that further human-assisted transfer both on Signy Island and beyond is avoided. Prof Bettine Jansen van Vuuren chaired the session of Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Biodiscovery.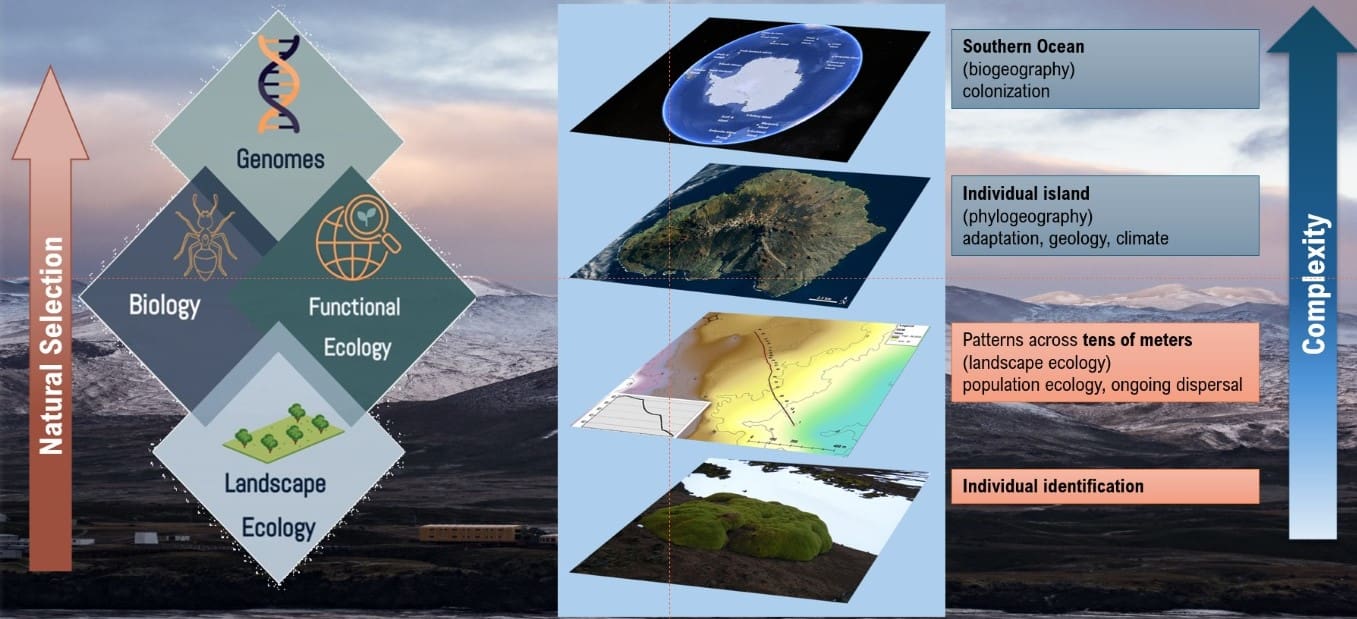 Bettine gave an overview of research that included research done by Daniela and Shilpha as they could not attend as they were on Marion Island. Foregrounding geodiversity in landscape ecology studies: insights from the sub-Antarctic – Daniela Monsanto (Abstract) Detecting signals of adaptive selection of an invasive springtail on sub-Antarctic Marion Island – Shilpha Parbhu (Abstract)
Bettine gave an overview of research that included research done by Daniela and Shilpha as they could not attend as they were on Marion Island. Foregrounding geodiversity in landscape ecology studies: insights from the sub-Antarctic – Daniela Monsanto (Abstract) Detecting signals of adaptive selection of an invasive springtail on sub-Antarctic Marion Island – Shilpha Parbhu (Abstract) Daniela Monsanto, Shilpa Parbhu, Sandra Durand, Arsalan Emami-Khoyi, Peter Teske, David Hedding
Daniela Monsanto, Shilpa Parbhu, Sandra Durand, Arsalan Emami-Khoyi, Peter Teske, David Hedding Morgan Raath-Kruger(left) and student of Peter le Roux at University of Pretoria gave an oral presentation and an introduction to her poster.
Morgan Raath-Kruger(left) and student of Peter le Roux at University of Pretoria gave an oral presentation and an introduction to her poster. Another abstract submitted but Carol Jacobs(right) could not present is on the biosecurity within the South African National Antarctic Programme. (Abstract)https://alp.lib.sun.ac.za/handle/123456789/29301
Another abstract submitted but Carol Jacobs(right) could not present is on the biosecurity within the South African National Antarctic Programme. (Abstract)https://alp.lib.sun.ac.za/handle/123456789/29301



 Vacancy for field researcher on Marion Island (March 2024 – May 2025) –
Vacancy for field researcher on Marion Island (March 2024 – May 2025) – The Department of Plant and Soil Sciences at the University of Pretoria is offering one suitably qualified candidate an opportunity to spend a year on Marion Island to measure various aspects of the impact of the house mouse on the diversity and function of the terrestrial ecosystems of Marion Island. This work will entail collecting baseline data, mostly on invertebrates and plants.
The Department of Plant and Soil Sciences at the University of Pretoria is offering one suitably qualified candidate an opportunity to spend a year on Marion Island to measure various aspects of the impact of the house mouse on the diversity and function of the terrestrial ecosystems of Marion Island. This work will entail collecting baseline data, mostly on invertebrates and plants.

















